MYOCARDITIS: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments


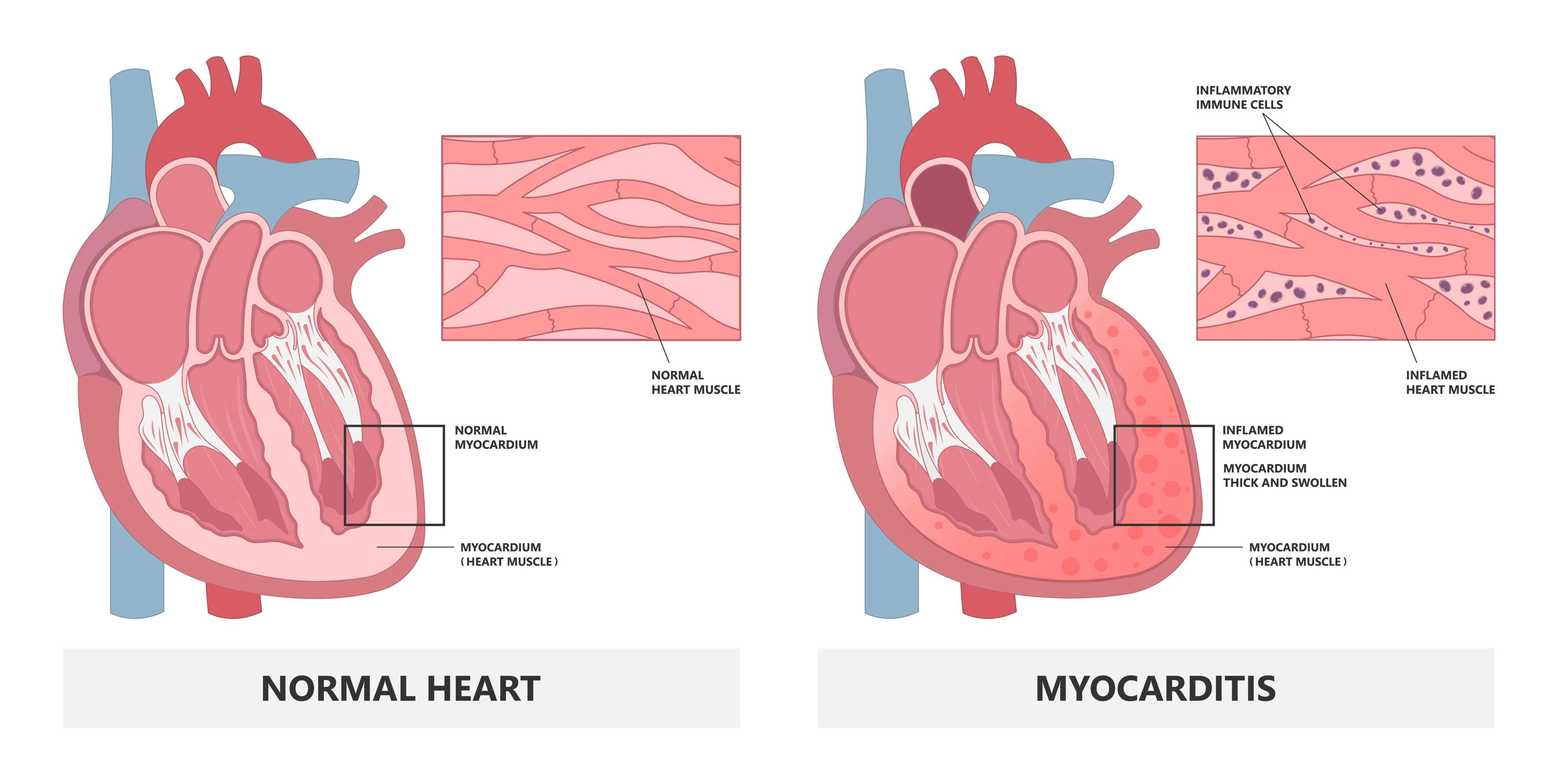
Myocarditis is a cardiac condition characterised by the inflammation of the heart muscle, also known as the myocardium. This inflammation can weaken the heart, affecting its ability to pump blood effectively. This article will explore the symptoms, causes, and available treatments for myocarditis.
What Is Myocarditis?
Myocarditis is a condition that involves the inflammation of the heart muscle. When the myocardium becomes inflamed, it can lead to various symptoms and complications. Understanding the symptoms and causes is essential to diagnose myocarditis.
Myocarditis Vs Pericarditis
Myocarditis and Pericarditis are both conditions involving inflammation of the heart, but they affect different parts of the heart. Myocarditis involves inflammation of the heart muscle itself (myocardium), while pericarditis is the inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart (pericardium). While they share some similar symptoms, such as chest pain and discomfort and may feel like a heart attack, they have distinct causes and treatments.
Viral infections or autoimmune reactions often cause myocarditis and can lead to heart muscle damage, potentially resulting in heart failure. On the other hand, pericarditis is commonly caused by viral infections or conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and typically results in chest pain exacerbated by breathing or movement but usually does not directly affect the heart muscle's pumping ability.
Types of Myocarditis
There are several types of myocarditis, each with distinct causes, clinical presentations, and implications for heart health. These conditions can damage the heart's electrical system, causing arrhythmias and potentially leading to severe complications if not treated promptly. Here, we will explain each type in detail:
Infectious Myocarditis
Causes: This is the most common type of myocarditis and is primarily caused by viral infections, including coxsackievirus, adenovirus, and enterovirus. Bacterial and fungal infections can also lead to infectious myocarditis which is also known as acute myocarditis.
Clinical Presentation: Patients with infectious myocarditis often experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and muscle aches. As the condition progresses, they may develop chest pain, shortness of breath, and irregular heart rhythms.
Implications: Infectious myocarditis can weaken the heart muscle and lead to heart failure if left untreated. It can also cause arrhythmias, which may be life-threatening in severe cases.
Autoimmune Myocarditis
Causes: Autoimmune myocarditis occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the heart muscle. It can be associated with autoimmune disorders like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis or may occur without an underlying autoimmune condition.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms can vary but often include chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Some individuals may experience symptoms related to the underlying autoimmune disorder.
Implications: This can occur due to more general inflammatory conditions such as autoimmune disorders, in which your immune system attacks healthy cells and tissue in your body.
Chronic Myocarditis
Causes: Chronic myocarditis is when it takes longer than usual to treat the disease or when symptoms reappear after experiencing the condition.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms can vary but often include chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Implications: This type of myocarditis is often resistant to treatment and can result in severe heart dysfunction. Heart transplantation may be necessary in some cases.
Giant Cell Myocarditis
Causes: Giant cell myocarditis is a rare and severe form of autoimmune myocarditis characterised by giant cells in heart tissue. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to have an autoimmune component.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms are similar to other types of myocarditis and may include chest pain, heart palpitations, and heart failure symptoms. Giant cell myocarditis can progress rapidly.
Implications: Autoimmune myocarditis can lead to heart muscle damage and heart failure if not managed appropriately. Treatment often involves immunosuppressive medications to dampen the immune response.
Hypersensitivity Myocarditis
Causes: Hypersensitivity myocarditis is typically triggered by exposure to certain medications, toxins, or allergens. Common culprits include drugs like antibiotics, antipsychotics, and some herbal supplements.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms may resemble those of other myocarditis types, with chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. A history of recent medication or toxin exposure is often a key clue.
Implications: Early recognition and discontinuation of the offending agent are crucial. In some cases, corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to manage inflammation.
Lymphocytic Myocarditis
Causes: Lymphocytic myocarditis is characterised by infiltrating lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) into the heart muscle. It can be associated with viral infections or autoimmune processes.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include chest pain, arrhythmias, and heart failure symptoms.
Implications: The prognosis for lymphocytic myocarditis varies depending on the extent of inflammation and heart damage. Treatment may involve medications to manage symptoms and inflammation.
Eosinophilic Myocarditis
Causes: Eosinophilic myocarditis is characterised by infiltrating eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, into the heart muscle. Various factors, including allergies, parasitic infections, and certain medications, can cause it.
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms may include chest pain, heart failure, and arrhythmias. The presence of eosinophils in blood or heart tissue is a diagnostic indicator.
Implications: Eosinophilic myocarditis can lead to significant heart damage if not addressed promptly. Identifying and treating the underlying cause is essential for management.
Symptoms
Myocarditis Symptoms
The symptoms of myocarditis can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms. Common symptoms of myocarditis include:
1. Chest Pain: This is one of the hallmark symptoms of myocarditis. The chest pain is typically described as a sharp or dull ache and can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. It may feel like a pressure or tightness in the chest and is often mistaken for a heart attack.
2. Fatigue: Many individuals with myocarditis experience extreme tiredness or fatigue, which can be debilitating and persistent. This fatigue may not improve with rest.
3. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying flat, is a common symptom of myocarditis. Some individuals may experience breathlessness even at rest.
4. Palpitations: Irregular heart rhythms or palpitations are another common symptom. You may feel that your heart is racing, skipping beats, or fluttering.
5. Swelling (Edema): Fluid retention can lead to swelling, typically in the legs, ankles, feet, and sometimes in the abdomen. This swelling is often due to the heart's reduced ability to pump blood effectively.
6. Flu-like Symptoms: Myocarditis can initially present with flu-like symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, joint pain, and fatigue. These symptoms can be misleading and may delay diagnosis.
7. Weakness: A feeling of weakness or malaise is often reported by individuals with myocarditis. This weakness can be severe and interfere with daily activities.
8. Rapid Breathing: Myocarditis can lead to an increased respiratory rate, especially during physical exertion.
9. Dizziness or Fainting (Syncope): In some cases, individuals with myocarditis may experience dizziness or fainting spells due to irregular heart rhythms or reduced blood flow to the brain.
10. Cough: A persistent, dry cough may occur as a result of fluid buildup in the lungs, known as pulmonary oedema.
11. Cyanosis: Cyanosis refers to a bluish tint of the skin, lips, or nail beds, which can occur when there is insufficient oxygen in the bloodstream.
It's important to note that the severity and combination of symptoms can vary among individuals with myocarditis. Some people may have mild symptoms and recover without significant complications, while others may experience severe heart dysfunction and complications like heart failure or arrhythmias.
Symptoms of Myocarditis in infants and Children
Symptoms of myocarditis in infants and children can vary and might not always be obvious. Common signs include difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, or laboured breathing. Infants may also exhibit poor feeding and lethargy.
In older children, symptoms can include abdominal pain, chest pain, or a feeling of general malaise. Fever is also a common symptom. Parents must be aware of these symptoms and consult a healthcare professional if their child shows any signs of myocarditis.
Causes
Causes of Myocarditis
Myocarditis can have various causes. It can result from viral infections, bacterial infections, or autoimmune diseases. Viral infections, in particular, are a common cause of myocarditis. Understanding the underlying cause of myocarditis is important for devising an appropriate treatment plan.
Myocarditis and Viral Infections
Viruses such as enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and parvovirus B19 are known to cause myocarditis. These viruses can infect the heart muscle, leading to inflammation. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect a viral infection that may be causing myocarditis.
Autoimmune conditions like lupus and sarcoidosis can also cause myocarditis, as the immune system has the potential to target and cause inflammation in any organ, including the heart. Additionally, myocarditis can be a result of exposure to drugs, environmental factors, or toxins.
COVID-19 and Myocarditis
Since 2021, there has been a growing concern about the association between COVID-19 and myocarditis. Some cases of myocarditis have been reported following COVID-19 infection or COVID-19 vaccination. It is essential to stay informed about the latest research and guidelines regarding COVID-19 and its potential impact on myocarditis.
Influenza A and Myocarditis
Influenza A, a subtype of the influenza virus, has been associated with an increased risk of myocarditis, characterised by heart muscle inflammation. While it typically presents with respiratory symptoms such as fever, cough, and body aches, in some cases, it can trigger an immune response that inadvertently targets the heart tissue, leading to myocardial inflammation. This inflammatory process can weaken the heart's ability to pump blood efficiently, resulting in chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath.
It's essential to recognize that influenza A-related myocarditis is rare but can be severe, particularly in vulnerable populations. Vaccination against influenza A is a crucial preventive measure to reduce the risk of influenza infection and its potential complications, including myocarditis. Early recognition of symptoms and medical intervention are vital for managing influenza A-related myocarditis effectively.
Influenza B and Myocarditis
Influenza B, another strain of the influenza virus, has also been associated with myocarditis. However, it is less commonly reported than Influenza A. Myocarditis can occur as a rare but potentially severe complication of an influenza B infection. The virus can trigger an inflammatory response in the heart muscle, leading to chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and irregular heart rhythms.
While the incidence of influenza B-related myocarditis is lower than that of Influenza A, it highlights the importance of vaccination against influenza to reduce the risk of infection and its potential complications. Individuals with underlying heart conditions or other risk factors should be especially vigilant during flu seasons and seek prompt medical attention if they experience cardiac symptoms or respiratory distress, as early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing influenza B-related myocarditis effectively.
Complications
Myocarditis can lead to various complications, including heart failure, dilated cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias. Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump blood effectively, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, fluid retention, and shortness of breath. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and weakened. Arrhythmias refer to abnormal heart rhythms and can have profound implications for overall cardiovascular health.
Diagnosis
How Is Myocarditis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing myocarditis involves a thorough evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. A cardiologist may order blood tests, chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, or cardiac MRI to assess the heart's function and identify signs of inflammation. These tests can reveal the condition's impact on the heart's electrical system and overall function.
Diagnostic Tests for Myocarditis
Various diagnostic tests can aid in the diagnosis of myocarditis. Blood tests can detect elevated levels of cardiac enzymes and markers of inflammation. An electrocardiogram (ECG) can reveal abnormal heart rhythms or other electrical disturbances. Echocardiogram and cardiac MRI provide detailed heart images, allowing the healthcare professional to assess its structure and function.
Treatment for Myocarditis
Managing and Treating Myocarditis
Myocarditis treatment depends on its severity and underlying cause. In mild cases, rest may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. In more severe cases, hospitalisation and specialised care, such as medications to support heart function or even a heart transplant, may be necessary.
In cases of myocarditis where a bacterial infection is identified as the underlying cause, the use of antibiotics may be necessary. Among these, Macrolide antibiotics are sometimes prescribed. They work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and aiding in treating the infection. However, it's crucial to have a proper diagnosis to determine the cause of myocarditis, as antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections. It is essential to consult with a cardiologist to devise an appropriate treatment plan for myocarditis.
Prevention
Preventing Myocarditis
Preventing myocarditis involves taking certain precautions to reduce the risk of infection. Practising good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with individuals with viral or bacterial infections, can help minimise the chances of contracting myocarditis. It is also important to stay up-to-date with recommended vaccinations, including the COVID-19 vaccine, as appropriate.
Research
Current Research on Myocarditis
Ongoing research is being conducted to understand further the causes, prevention, and treatment of myocarditis. Scientists and healthcare professionals are exploring new diagnostic techniques, potential therapeutic options, and the long-term effects of myocarditis. Staying informed about current research can provide valuable insights into advancements in myocarditis management.
Frequently Asked Questions About Myocarditis
Many people have questions about myocarditis, its symptoms, and treatment options. Some frequently asked questions about myocarditis include the following:
What Is Myocarditis?
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle, specifically the middle layer called the myocardium.
What Are the Symptoms of Myocarditis?
The symptoms of myocarditis may vary, but common symptoms include chest pain, fever, fatigue, shortness of breath, and swollen legs or ankles. People with myocarditis tend to also have symptoms of heart failure.
What Causes Myocarditis?
Myocarditis can be caused by viral infections, such as the flu or COVID-19, as well as bacterial or fungal infections. It can also be caused by certain medications, toxins, or autoimmune diseases. It is also important to keep in mind that myocarditis affects people of all ages and at times, myocarditis can develop suddenly.
Is Viral Myocarditis a Common Form of Myocarditis?
Yes, viral myocarditis is one of the most common causes of myocarditis. Viral infections, such as enteroviruses and adenoviruses, can lead to inflammation of the heart muscle.
What Is the Relationship Between COVID-19 and Myocarditis?
COVID-19 has been associated with cases of myocarditis, especially in individuals who have had severe or prolonged illness. It is important to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention if there are concerns about myocarditis following a COVID-19 infection or vaccination.
How Is Myocarditis Diagnosed?
Myocarditis may be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests (such as echocardiogram or MRI), and heart biopsy in some cases.
What Are the Treatment Options for Myocarditis?
The treatment for myocarditis depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. It can include rest, lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress as well as medication to reduce inflammation, managing symptoms, and treating complications. In severe cases, advanced treatments such as heart transplants may be necessary.
Is There Research Being Done on Myocarditis?
Yes, there is ongoing research focused on understanding the causes, mechanisms, and treatment options for myocarditis. This research aims to improve diagnosis, prognosis, and long-term outcomes for individuals with myocarditis.
Can Myocarditis Lead to Heart Failure?
Yes, in some cases, myocarditis can lead to heart failure. The inflammation weakens the heart muscle, affecting its ability to pump blood effectively, which can result in heart failure.
Are There Any Organizations or Resources I Can Consult to Learn More About Myocarditis?
The American Heart Association, as well as other reputable healthcare organizations such as the Singapore Heart Foundation, provide information and resources on myocarditis. You can also consult with your healthcare provider for more specific information related to your situation.
Conclusion
The Harley Street Heart & Vascular Centre in Singapore is your trusted partner in myocarditis care. With a team of top cardiologists and advanced facilities, we provide expert diagnosis and treatment for heart conditions, including myocarditis. Our patient-centred approach ensures you receive the best care and support on your heart health journey. For top-notch cardiac care in Singapore, schedule your consultation with us today and prioritize your heart's well-being. Your heart deserves nothing but the best, and we're here to provide it.