Arteriosclerosis: Understanding Its Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Arteriosclerosis is often perceived as a complex medical term, that fundamentally refers to the hardening of the arteries. This condition is pivotal in the discussion of cardiovascular health due to its widespread impact and the critical role it plays in various heart-related diseases. Understanding arteriosclerosis is not just about recognising a medical condition; it's about acknowledging a significant health challenge that affects millions globally. In this article, we delve deep into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for arteriosclerosis, aiming to equip you with knowledge and strategies to manage or prevent this condition effectively.
What is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries. This process restricts blood flow to your organs and tissues, potentially leading to severe health complications. Several factors contribute to the development of arteriosclerosis, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. These risk factors damage the inner layer of the artery, leading to the build-up of plaque—a combination of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood.
Types of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis manifests in several forms, each affecting the arteries in different ways:
- Atherosclerosis involves the buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls.
- Arteriolosclerosis affects the smaller arteries and arterioles, leading to thickening and stiffening of their walls.
- Mönckeberg medial calcific sclerosis is characterized by the calcification of the muscular middle layer of the arteries.
Understanding these types is crucial for diagnosing and treating the specific form of arteriosclerosis an individual may have.
Atherosclerosis: The Common Culprit
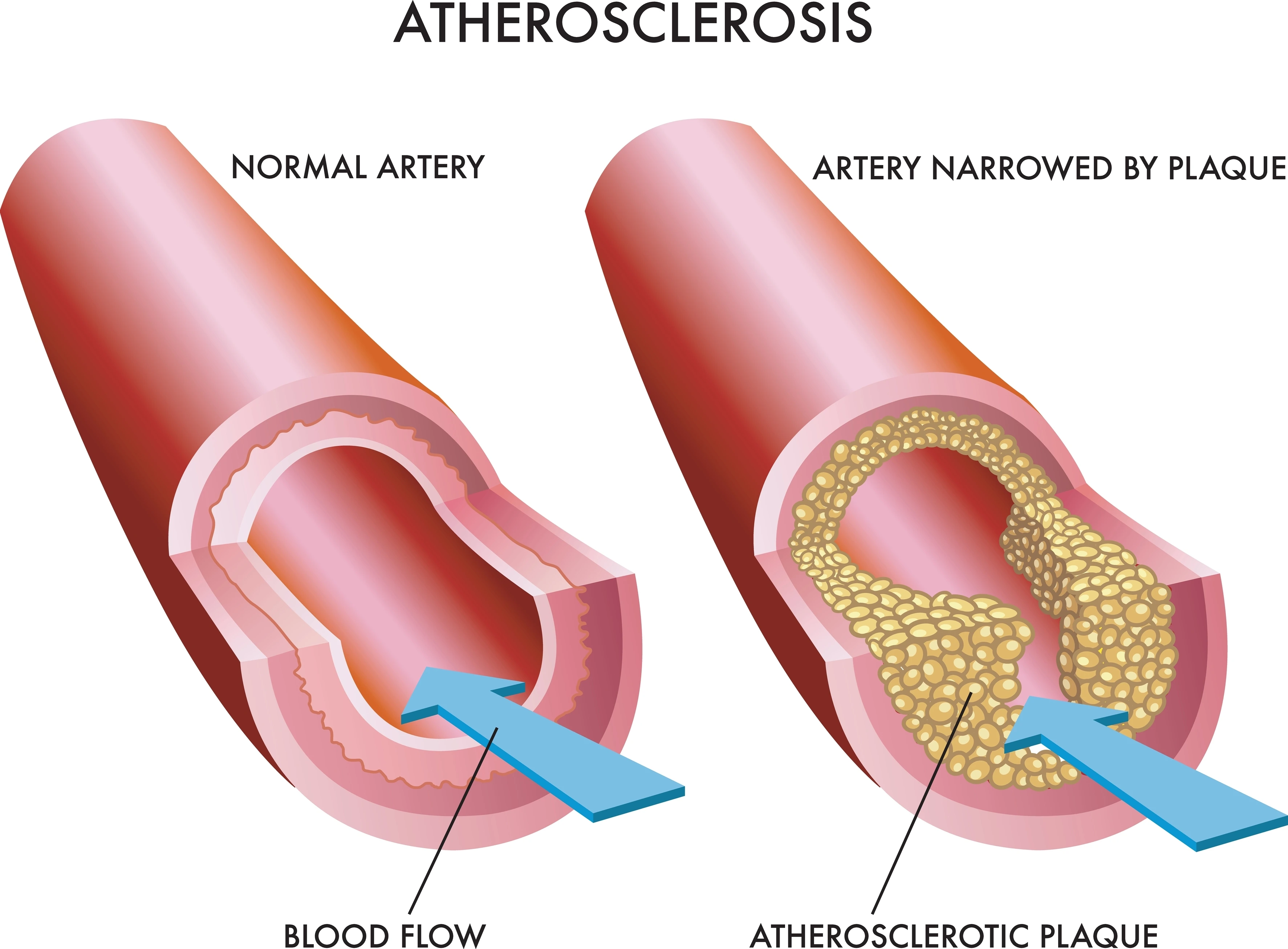
Atherosclerosis is the most recognised form of arteriosclerosis and is often the primary focus when discussing heart disease. It occurs when fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances build up in the inner lining of an artery. This buildup is known as plaque. Over time, these plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, severely limiting the flow of oxygen-rich blood to organs and tissues.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of atherosclerosis is complex and multifactorial, involving:
- High levels of "bad" cholesterol (LDL) and low levels of "good" cholesterol (HDL)
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
Health Implications
Atherosclerosis can lead to serious health problems, including heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease, depending on which arteries are blocked.
Arteriolosclerosis: The Small Artery Challenger
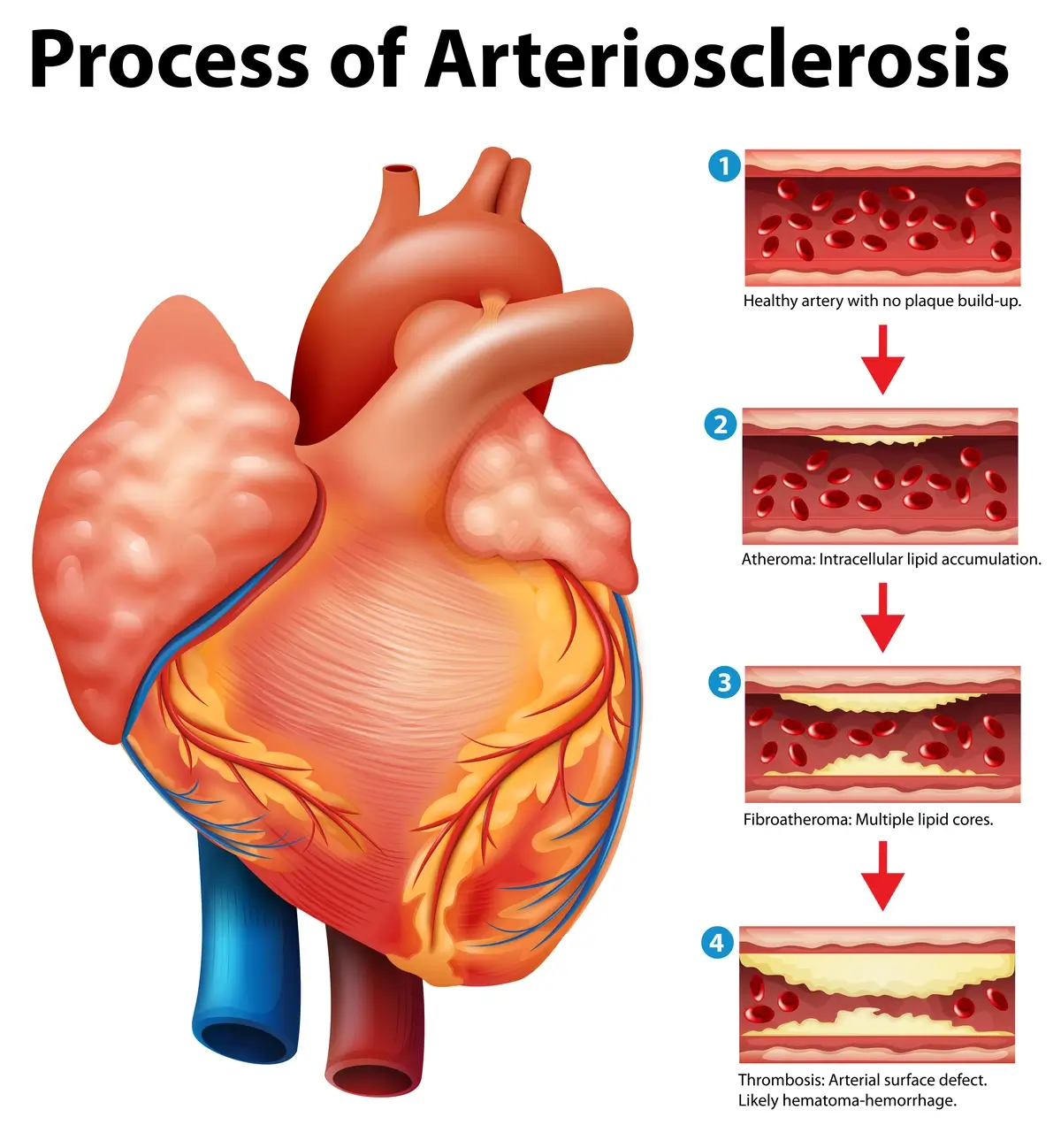
Arteriolosclerosis specifically affects the small arteries, known as arterioles, which play a crucial role in regulating blood flow to tissues. In this condition, the arterioles become thickened and stiff, a process that can be accelerated by high blood pressure and diabetes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Key factors contributing to arteriolosclerosis include:
- Chronic high blood pressure, which exerts excessive force against the arterial walls
- Diabetes, which can damage blood vessels over time
- Aging, as the blood vessels naturally lose elasticity
Health Implications
Arteriolosclerosis can lead to reduced blood flow to organs and tissues, potentially resulting in conditions like chronic kidney disease and hypertensive heart disease.
Mönckeberg Medial Calcific Sclerosis: The Calcification Condition
Mönckeberg medial calcific sclerosis is less common and involves the calcification of the muscular middle layer of the arteries, rather than the inner lining. This type of arteriosclerosis does not typically obstruct blood flow as much as the others but can indicate underlying vascular disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Mönckeberg medial calcific sclerosis is not well understood, but it is more frequently observed in individuals with diabetes and those over the age of 50.
Health Implications
While it may not directly lead to significant blood flow reduction, its presence can be a marker for other vascular diseases and overall cardiovascular risk as it is a challenge for blood to flow to your heart.
Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis
The symptoms of arteriosclerosis can vary widely depending on the affected artery. Common signs include:
- Chest pain or angina
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion, if the arteries supplying the brain are affected
- Muscle weakness or numbness, if blood supply to certain parts of the body is reduced
Early detection of these symptoms can lead to a timely diagnosis and treatment, potentially averting more severe complications of cardiovascular disease such as heart attack or stroke.
Diagnosing Arteriosclerosis
Diagnosis of arteriosclerosis involves a combination of physical exams, medical history evaluation, and specific diagnostic tests. These may include blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, and imaging tests like angiography, which provides detailed images of the arteries.
Treatment Options
Treatment for arteriosclerosis focuses on symptom management and slowing the progression of the disease. Arteriosclerosis treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgical procedures. Early diagnosis and treatment medications may be prescribed to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and prevent blood clots, heart attack and stroke. Surgical options, such as angioplasty and artery bypass surgery, are considered for severe cases to restore adequate blood flow to the heart.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing arteriosclerosis involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle such as:
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
- Reducing the intake of oily and processed food
- Keeping your sugar and cholesterol levels under control
- Minimise the intake of sugary and carbonated drinks
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels
These measures not only help prevent arteriosclerosis but also contribute to overall health and well-being. While there are different causes of arteriosclerosis, such as a family history of heart disease, these measures help keep the arteries healthy and can reduce aggressive treatment to stop arteriosclerosis. The management and treatment of your heart's health is crucial.
Comparison: Arteriosclerosis vs. Atherosclerosis
While arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. The key difference lies in the specific changes happening within the arteries, with atherosclerosis specifically referring to the buildup of plaque in the coronary artery that can lead to blockages and if not treated can lead to heart attack or heart failure.
Conclusion
Arteriosclerosis is a significant health concern with the potential to lead to life-threatening conditions. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for prevention and management. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and seeking early medical intervention, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing arteriosclerosis and maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
Frequently Asked Questions About Arteriosclerosis
What Is the Difference Between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis refers to the general hardening and thickening of the arteries, while atherosclerosis specifically describes the buildup of plaques within the arterial walls. Atherosclerosis affects the supply of blood to your heart and increases the risk of heart disease.
What Are the Symptoms of Arteriosclerosis?
Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, confusion, and muscle weakness or numbness, depending on the arteries affected. Arteriosclerosis affects small arteries and arterioles as it disturbs the electrical activity of the heart and forces the heart to work harder.
How Is Arteriosclerosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, a review of medical history, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, ECG, stress tests, and imaging procedures. If you detect signs of arteriosclerosis, you can also check for atherosclerosis with The Harley Street Heart & Vascular Centre.
Are There Any Natural Remedies for Managing Arteriosclerosis?
While lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation are crucial, it's important to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive treatment plan.


