HEART RHYTHM DISORDERS

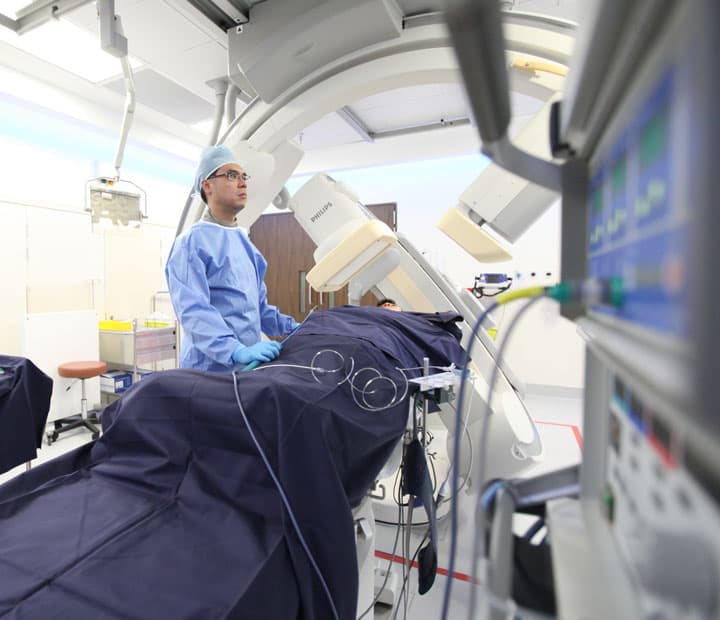
Similar to keyhole surgery, under light sedation, catheters are inserted in a blood vessel in the leg that enter the heart.

For complex heart rhythm disorders, this treatment provides more information on the heart’s anatomy and electrical activity.
When electrical impulses which coordinate your heartbeats don't work properly, heart rhythm problems arise. This makes your heart beat too fast, too slow or irregularly.
In cases which cannot be treated with medication, a minimally invasive procedure (electrophysiological study & catheter ablation) can determine effective treatment. In some cases, catheter ablation can be curative, thus avoiding lifelong medication. It can take less than an hour or just over four hours to perform, depending on the type of heart rhythm disorder.
For complex disorders, a special 3-dimensional mapping system is often used to display more information on the anatomy and electrical activity of the heart - this helps guide the procedure to improve the accuracy and outcome.
Electrophysiology (EP) Study & Catheter Ablation
Some types of heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias) cannot be treated adequately with medication, in which case an electrophysiological (EP) study and catheter ablation procedure may be required.
This is a minimally invasive procedure (similar to keyhole surgery) in which the cardiologist inserts thin flexible wires (called catheters) a blood vessel in the leg into the heart. Electrical stimulation of the heart through the carefully placed catheters usually allows the exact arrhythmia to be diagnosed. High-frequency electrical energy can then be delivered by the cardiologist through one of the catheters during ablation to a small area of tissue inside the heart to destroy the part that is causing the arrhythmia. Catheter ablation can be curative for some types of arrhythmias and avoid the need for lifelong medication.
The procedure can range from under one hour to more than four hours depending on the type and complexity of the arrhythmia and is usually performed using light sedation. A special 3-dimensional mapping system is often used by the cardiologist for the treatment of complex heart rhythm disorders (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia) as this provides more information on the anatomy and electrical activity of the heart.