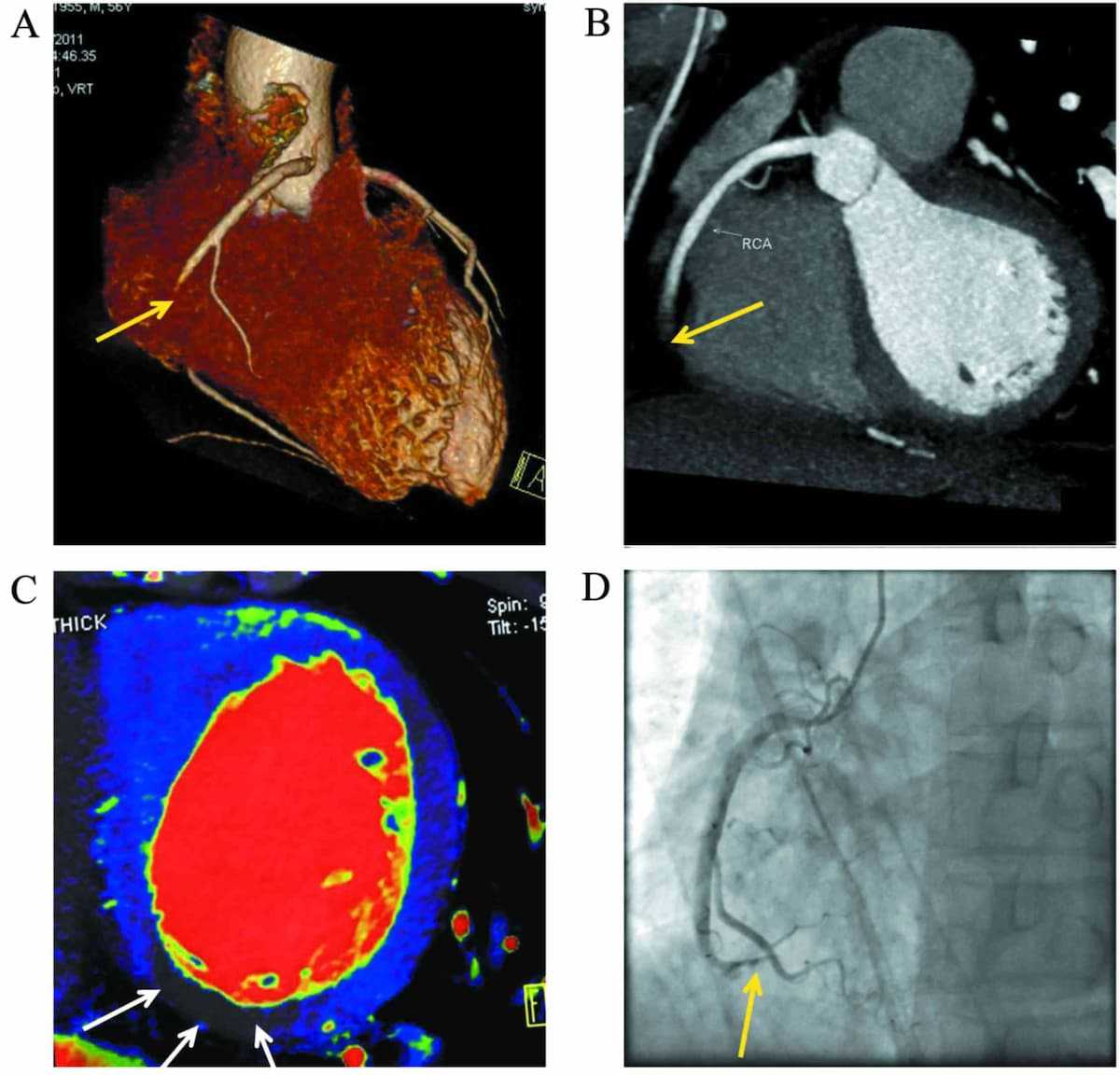
ANEURYSM REPAIR
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal widening of the blood vessel due to a weakening of the wall. They can be clinically silent and not cause any symptoms but nonetheless be potentially dangerous and rupture if they increase to a certain size. Thoracic aortic aneurysms can be treated by the cardiothoracic surgeon through an open chest operation or endovascular approach. The operation involves the insertion of an artificial graft into the abnormal blood vessel to cover the diseased section either directly (open operation) or percutaneously with a balloon and stent through a blood vessel in the leg (endovascular approach).

Frequently Asked Questions
While information online about Aneurysm Repair may be useful and informative, it is best to always consult a medical professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Here are some frequently asked questions:
How is thoracic aortic aneurysm treated?
Treatment for thoracic aortic aneurysms typically involves either open-chest surgery or an endovascular approach. Open surgery requires a large incision to replace the damaged aorta segment with a graft, while endovascular repair uses a catheter inserted through the groin to place a stent graft, offering a less invasive alternative with a shorter recovery time.
What is the recovery time after aneurysm repair?
Recovery duration varies based on the surgical method. Open surgery patients may stay in the hospital for 5–7 days, with full recovery taking several weeks to months. Endovascular repair usually entails a shorter hospital stay of 1–2 days and a quicker return to normal activities, often within a week, depending on individual health factors.
What are the risks of aneurysm surgery?
Aneurysm repair carries potential risks, including bleeding, infection, blood clots, and anaesthesia-related complications. Open surgery may have higher risks due to its invasive nature. In contrast, endovascular repair, though less invasive, can lead to issues like endoleaks or stent migration. Patient-specific factors such as age and overall health also influence risk levels.
When is aneurysm repair necessary?
Aneurysm repair becomes necessary when the aneurysm reaches a size or growth rate that significantly increases the risk of rupture. Typically, surgical intervention is considered for aneurysms larger than 5.5 centimetres or those expanding rapidly. Symptoms like pain or evidence of dissection also warrant prompt surgical evaluation.
What lifestyle changes are recommended after aneurysm repair?
Post-surgery, adopting heart-healthy habits is crucial. Recommended changes include quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet low in saturated fats, regularly exercising regularly, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests are essential to monitor the repair site and overall vascular health.