Medications For Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia, a condition characterised by irregular heart rhythms, requires careful management to ensure optimal cardiac health. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the common medications used to treat arrhythmia, their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and when they should be considered. Our goal is to provide a resource that not only informs but also positions itself as an authoritative piece to assist individuals seeking insights into arrhythmia medication.
Read more about it below or you may book an appointment for a cardiac evaluation with one of our cardiologists or contact us for further details to schedule your test.
What Are the Common Medications Used to Treat Arrhythmia?
The treatment of arrhythmia has seen significant progress thanks to advancements in medical science. Commonly utilised medications include beta-blockers, which slow your heartbeat, calcium channel blockers, which help to relax heart muscles, and sodium channel blockers and potassium channel blockers which regulate the heart's electrical activity. Anticoagulants are also used to reduce the risk of blood clots. Always remember, your healthcare team is knowledgeable and here to help! Taking prescribed medications regularly and having open communication with your doctors will significantly aid in managing your arrhythmia efficiently.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Antiarrhythmic drugs are a class of medication used to manage abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation and atrial flutter. These drugs work by regulating the electrical activity of the heart to maintain a normal rhythm and prevent potential complications. They are commonly prescribed to patients with conditions such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, atrial flutter, and atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia.
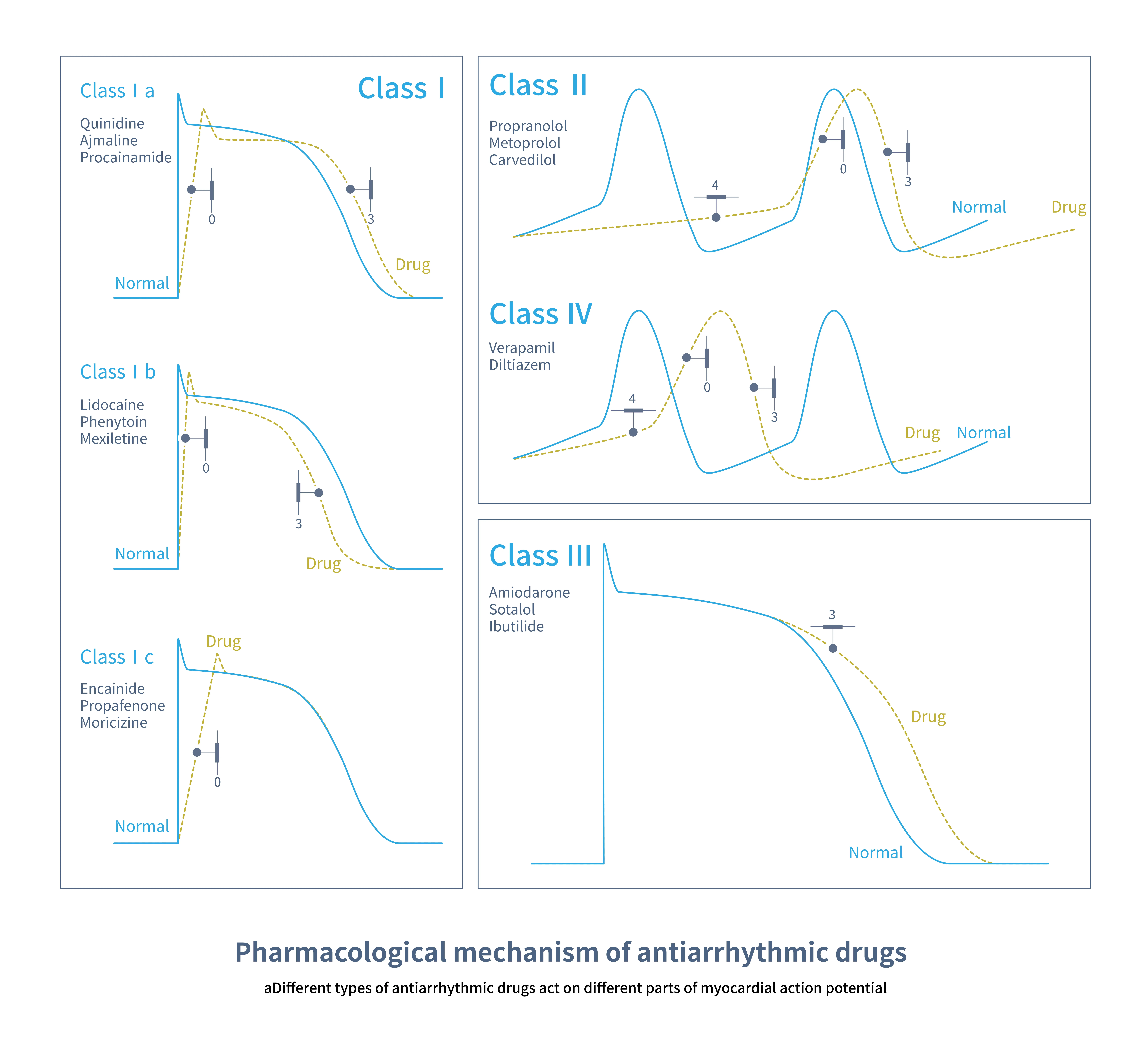
Class I Antiarrhythmic Drugs
In the realm of antiarrhythmic medications, Class I drugs play a crucial role in managing irregular heartbeat. By interfering with sodium channels, they modulate electrical impulses, stabilising heart rhythms. Some of the common Class I antiarrhythmic drugs are disopyramide, flecainide, lidocaine, mexiletine, quinidine, procainamide, and propafenone, which are mostly used for various atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Class II Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Beta-blockers, falling under Class II, exert their influence by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart. This reduction in stress hormones helps control heart rate and rhythm. Class II antiarrhythmic drugs are useful for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardias.
Class III Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Class III drugs primarily affect potassium channels, prolonging the duration of electrical signals. This action aids in preventing abnormal rhythms and maintaining a steady heartbeat. Amiodarone, dofetilide, ibutilide, and sotalol are the common Class III antiarrhythmic drugs.
Class IV Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Calcium channel blockers, falling under Class IV, impede the entry of calcium into the heart cells, effectively regulating heart rhythm.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers represent essential components of arrhythmia management, each with its unique mechanism of action. Some of the common calcium channel blockers are:
- Amlodipine
- Diltiazem
- Felodipine
- Isradipine
- Nicardipine
- Nifedipine
- Nisoldipine
- Verapamil
Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers on Heart Rhythm
Calcium channel blockers, by inhibiting calcium entry into heart cells, relax blood vessels and decrease the heart's workload. This dual action contributes to overall heart rhythm stability.
Beta Blockers
Understanding the impact of beta blockers on heart rate, particularly in conditions like a fast heart (tachycardia) and heart valve issues, is crucial in appreciating their role in arrhythmia treatment. Beta-blockers target beta receptors, reducing the heart's response to adrenaline. This results in a slowed heart rate and diminished force of contraction, which is essential in managing arrhythmias, including those related to fast heart and heart valve complications. Some of the common beta blockers used are:
- Metoprolol
- Atenolol
- Propranolol
- Carvedilol
- Bisoprolol
- Labetalol
- Nebivolol
- Nadolol
- Acebutolol
- Timolol
- Sotalol
- Betaxolol
- Esmolol
- Pindolol
- Penbutolol
Blood Thinners
In arrhythmia treatment, blood thinners play a pivotal role in preventing clot formation and reducing the risk of serious complications. Blood thinners, or anticoagulants, interfere with the blood clotting process, mitigating the risk of thrombus formation. This is particularly crucial in arrhythmia cases where blood flow irregularities pose heightened risks.
Types of common anticoagulants are:
- Apixaban
- Dabigatran
- Dalteparin
- Edoxaban
- Enoxaparin
- Fondaparinux
- Heparin
- Rivaroxaban
- Warfarin
And the types of common antiplatelets are:
- Aspirin
- Cilostazol
- Clopidogrel
- Dipyridamole
- Prasugrel
- Ticagrelor
- Vorapaxar
What Are the Potential Side Effects of Antiarrhythmic Medications?
Understanding the potential side effects of antiarrhythmic medications is essential for informed decision-making.
Possible Side Effects of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Antiarrhythmic drugs, while effective, may entail certain side effects. It's imperative to be aware of these potential repercussions, which can include dizziness, nausea, and, in rare cases, more severe complications like allergic reactions.
Possible Side Effects of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, though widely prescribed, may come with side effects such as fatigue, cold extremities, and in some instances, disruptions in sleep patterns. Monitoring for these effects is essential for optimal patient care.
Possible Side Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers might lead to side effects like headaches, oedema, and constipation. These reactions, though often mild, should be communicated to healthcare providers to ensure proper adjustments to the treatment plan.
Possible Side Effects of Blood Thinners
Blood thinners, while vital for preventing clots, may pose risks of bleeding. Close monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are imperative to strike a balance between efficacy and safety. Some of the lesser-known side effects of blood thinners include heavier menstrual bleeding for women, blood in urine or poop, coughing up blood or bloody sputum, dizziness, and fatigue among others.
How Do Antiarrhythmic Medications Work?
Class I drugs interfere with sodium channels, Class II with beta receptors, Class III with potassium channels, and Class IV with calcium channels. This intricate modulation ensures precise control over heart rhythms.
Mechanism of Action of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Antiarrhythmic drugs intervene at the cellular level, modulating ion channels and receptors to restore or maintain a normal heart rhythm. Understanding these mechanisms is pivotal in appreciating the nuanced approach to arrhythmia management.
Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers on Heart Rhythm
Calcium channel blockers, by impeding calcium influx, exert a controlled influence on heart rhythm. This delicate balance is essential in preventing arrhythmias without compromising the heart's overall function.
Impact of Beta Blockers on Heart Rate
Beta-blockers precisely targets the heart's beta receptors, regulating the organ's response to adrenaline and promoting a controlled heart rate. This precision is instrumental in managing various arrhythmic conditions.
Mode of Action of Blood Thinners in Preventing Blood Clots
Blood thinners act by inhibiting clot formation, thus reducing the risk of complications such as strokes. Understanding the mode of action is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
When Should a Person Consider Taking Antiarrhythmic Medications?
When dealing with irregular heart rhythms, known as arrhythmia, individuals may need to consider taking antiarrhythmic medications as a part of their treatment plan. These medications can help to control and stabilise the heart's rhythm, reducing the risk of potentially dangerous complications. However, determining the right time and circumstances for starting antiarrhythmic medications should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Factors Indicating the Need for Antiarrhythmic Therapy
Several factors may indicate the need for antiarrhythmic therapy, including the type and severity of the arrhythmia, the patient's overall health, and the potential risks associated with the condition.
Conditions Requiring the Use of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Various cardiac conditions necessitate the use of antiarrhythmic drugs, ranging from atrial fibrillation to ventricular tachycardia. Tailoring treatment to the specific condition is essential for optimal outcomes.
Indications for Calcium Channel Blockers and Beta Blockers
Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers are commonly prescribed medications used for the management of various cardiovascular conditions. Both classes of drugs are known for their ability to reduce blood pressure, control heart rate, and alleviate symptoms of certain heart-related conditions. Understanding the indications for these medications is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Instances Where Blood Thinners Are Necessary for Managing Arrhythmia
Blood thinners come into play, particularly in cases of cardiac arrhythmias associated with atrial fibrillation, where the risk of clot formation is heightened. Their use is a preventive measure to safeguard against potentially life-threatening complications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Arrhythmia Medications
What Is the Best Medication for Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is a serious condition that can lead to heart palpitations, fainting, and even sudden cardiac arrest. Determining the best medication for arrhythmia involves a thorough evaluation of the specific type of arrhythmia, the patient's overall health, and any potential contraindications. Consulting with a cardiology doctor is crucial for personalised recommendations.
What Is the Best Antiarrhythmic Drug?
Arrhythmias can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, and identifying the best antiarrhythmic drug is crucial in managing this disorder. With numerous options available, it's important to understand the effectiveness and potential risks of each medication to ensure the best possible outcome for those suffering from these cardiac disturbances.
What Are First Line Treatment of Arrhythmias?
First-line treatments for arrhythmias often involve the use of Class I or Class III antiarrhythmic drugs, depending on the specific nature of the irregular heart rhythm. This strategic approach aims for effective control with minimal side effects. However, for some arrhythmias catheter ablation is the first line treatment.
What Is the Most Common Treatment for Arrhythmias?
The most common treatment for arrhythmias often involves the use of beta blockers and calcium channel blockers. These medications, when prescribed judiciously, contribute to stabilising heart rhythm and improving overall cardiac health.
What Is the Safest Antiarrhythmic Drug?
Determining the safest antiarrhythmic drug involves considering the specific arrhythmia, the patient's overall health, and any potential interactions with other medications. Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for monitoring safety.
Which Beta Blocker Is Best for Arrhythmia?
The choice of the best beta blocker for arrhythmia depends on factors such as the patient's overall health, the type of arrhythmia, and any existing medical conditions. Tailoring treatment ensures the best possible outcome.
What Medication Lowers Heart Rate Immediately?
In situations where an immediate reduction in heart rate is necessary, medications like beta blockers or calcium channel blockers may be considered. However, the choice depends on the specific circumstances and should be guided by a cardiology clinic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the landscape of arrhythmia medications requires a nuanced understanding of each drug's mechanism of action, potential side effects, and specific indications. At The Harley Street Heart and Vascular Centre, our team of dedicated cardiologists is at the forefront of innovative cardiac care. With state-of-the-art facilities and a commitment to personalised treatment, we prioritise your heart's health above all else. Book an appointment or teleconsultation today to put your heart's well-being first.

