Atrial Septal Defect: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment


Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart condition that affects thousands of individuals across the globe. Despite often being asymptomatic in early life, untreated ASDs can lead to severe cardiovascular complications in adulthood..
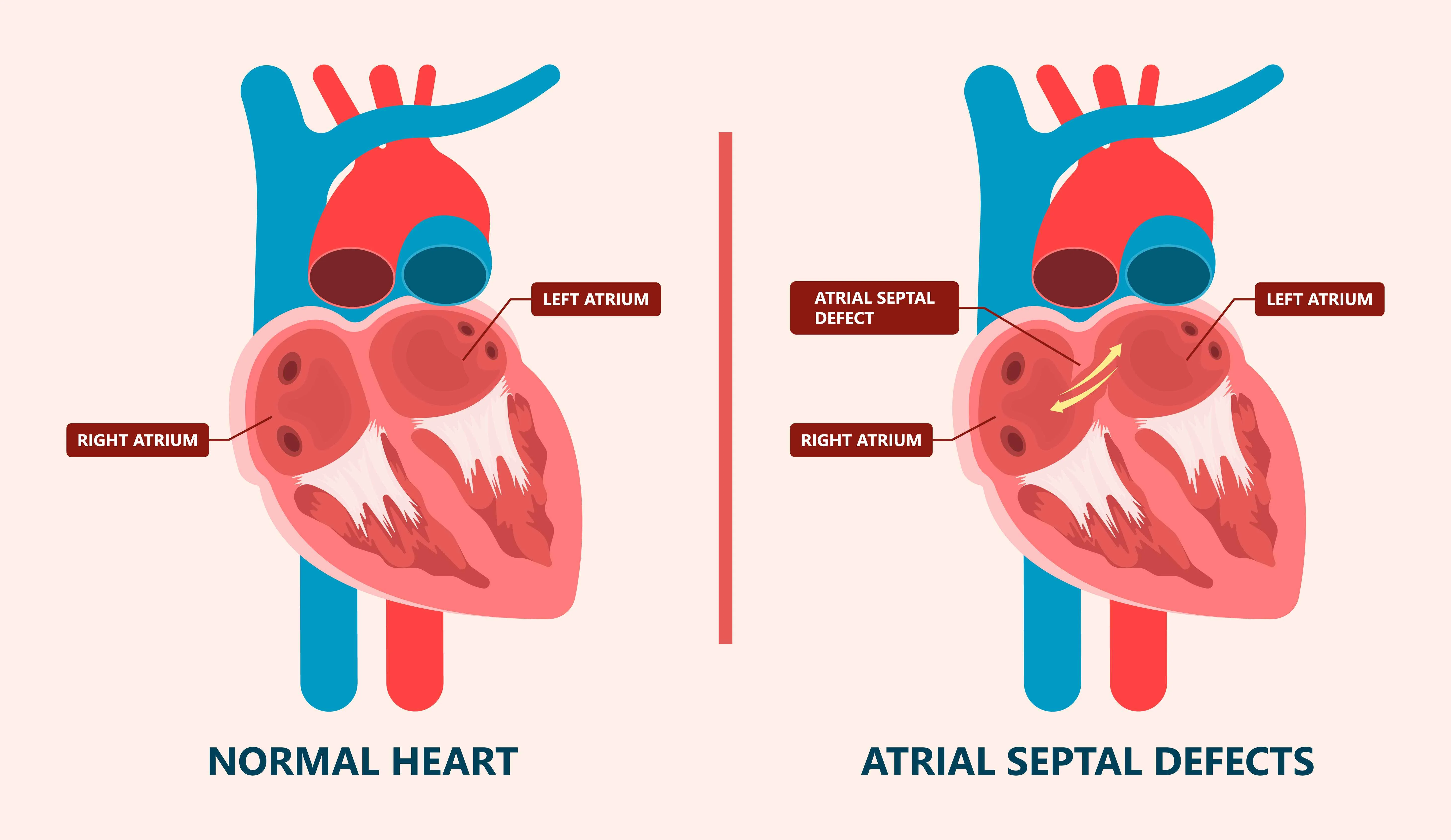

What is an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)?
An atrial septal defect is an opening in the septum, the wall separating the heart's two upper chambers (atria). This defect allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to mix with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium, leading to inefficient blood circulation and potential complications over time.
Types of Atrial Septal Defects
- Ostium Secundum ASD: The most common type, located in the middle of the atrial septum.
- Ostium Primum ASD: Found in the lower part of the atrial septum and often associated with other congenital anomalies.
- Sinus Venosus ASD: A rarer form near the veins that bring blood back from the lungs.
- Coronary Sinus ASD: Extremely rare, involving the coronary sinus.
Expert Insight: Cleveland Clinic notes sinus venosus atrial septal defects are often linked with defects in the right pulmonary vein or superior or inferior vena cava, pointing to associated vascular abnormalities.
Causes and Risk Factors
ASDs are congenital, meaning they are present at birth. The exact cause of these defects is often unknown but may involve genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
- Family history of congenital heart defects
- Genetic syndromes such as Down syndrome
Environmental Risk Factors
- Maternal diabetes
- Rubella infection during pregnancy
- Substance use (alcohol, certain medications, smoking)
Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
Many individuals with ASD experience no symptoms during childhood. However, symptoms may manifest later in life, especially if the defect is large or untreated.
Common Symptoms
- Shortness of breath, particularly during exercise
- Fatigue
- Heart palpitations or skipped beats
- Swelling of the legs, feet, or abdomen
- Frequent respiratory infections in children
- Stroke (in rare cases)
Symptom Highlight: The American Heart Association mentions that a common sign of ASD is a heart murmur which a healthcare provider might hear when listening to the heart.
How ASD Affects the Heart
Oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood mix in the atria, forcing the heart and lungs to work harder. Over time, this may result in:
- Enlargement of the right side of the heart
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Heart failure
Diagnosis of Atrial Septal Defect
Physical Examination
Many ASDs are discovered during routine check-ups. A heart murmur may prompt further investigation.
Diagnostic Tests
- Echocardiogram: The most definitive diagnostic tool. A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) offers a more detailed view.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Helps identify arrhythmias.
- Chest X-ray: May show an enlarged heart or abnormal lung blood vessels.
- Cardiac MRI: Provides detailed images of heart structures.
- Cardiac catheterisation: Occasionally used for diagnostic confirmation
Diagnostic Detail: he American Heart Association specifies that if an ASD is suspected, the most common test used to confirm it is an echocardiogram, which uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart.
Treatment Options for ASD
Treatment choice depends on the defect's size, symptoms, patient age, and presence of complications.
Monitoring
Small ASDs without symptoms may not require immediate treatment. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure the defect does not enlarge.
Medications
Medications do not close the defect but may manage symptoms and associated complications such as:
- Antiarrhythmics
- Beta-blockers
- Diuretics
- Anticoagulants (if there's a risk of stroke)
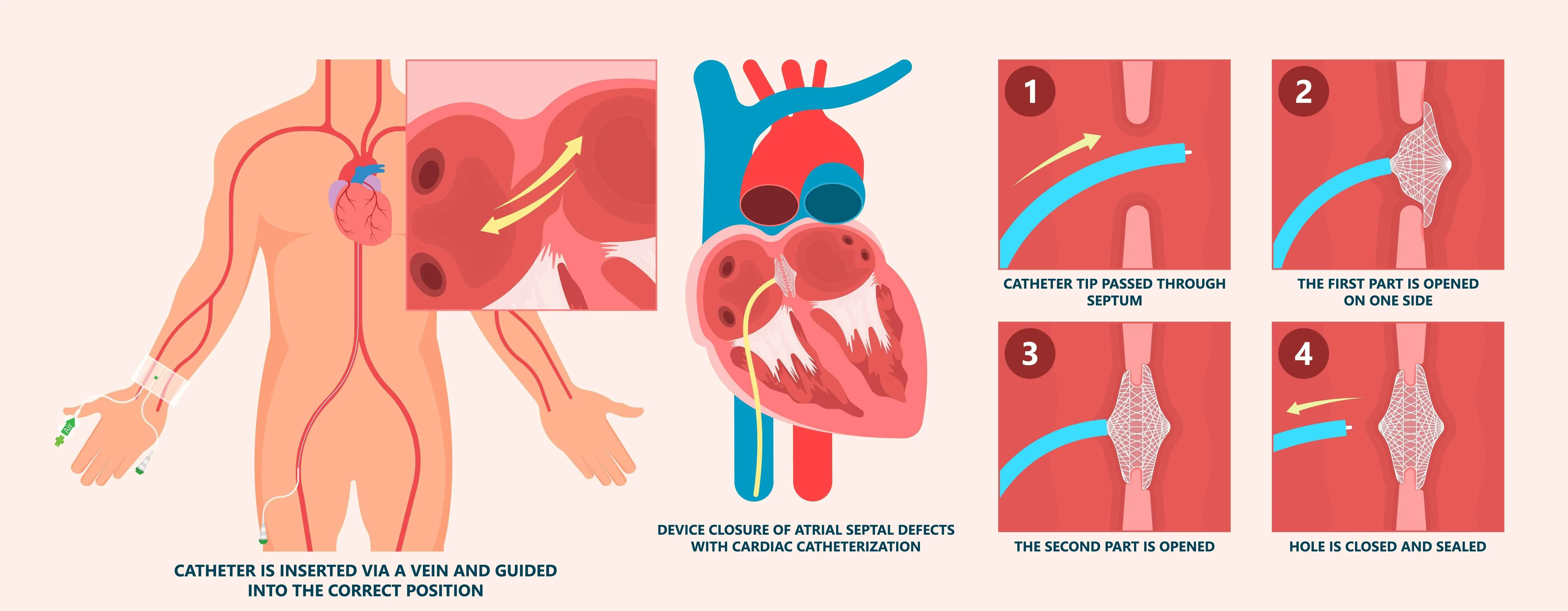

Catheter-Based Closure
A minimally invasive procedure where a device is inserted through a vein in the leg to close the defect. This is suitable for many secundum ASDs.
Surgical Repair
Open-heart surgery may be necessary for:
- Large ASDs
- ASDs are not suitable for catheter-based repair
- Associated heart defects
This procedure involves suturing the defect or placing a patch over it. Surgical repair has a high success rate and is generally safe.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
With appropriate treatment, individuals with ASD can live normal, healthy lives. Early diagnosis and timely intervention are key to preventing complications.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Right-sided heart failure
- Stroke due to paradoxical embolism
- Arrhythmias
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
Regular follow-up with a cardiologist is crucial to:
- Monitor heart function
- Ensure the device or surgical repair is intact
- Manage any arising complications
Living with an Atrial Septal Defect
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Regular exercise (as recommended by your doctor)
- A Healthy die
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol
- Managing comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes
Pregnancy Considerations
Women with repaired ASDs typically have successful pregnancies. However, those with untreated or complex ASDs should undergo thorough evaluation and monitoring during pregnancy.
ASD in Children vs. Adults
In Children
- Often asymptomatic
- Detected through routine pediatric check-ups
- Excellent outcomes with early repair
In Adults
- May present with complications
- Diagnosis often delayed
- Timely intervention can still yield positive outcomes
Conclusion
The atrial septal defect is a manageable congenital heart condition when detected and treated appropriately. Our heart clinic emphasises early detection, personalised care plans, and long-term follow-up to ensure our patients achieve optimal cardiac health. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with ASD, we are here to provide compassionate, expert care tailored to your needs.
Contact us for more information or to book an appointment.
This write-up has been medically reviewed by Dr. Michael Ross MacDonald, a consultant cardiologist at The Harley Street Heart & Vascular Centre in Singapore, to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.