Atrioventricular Block: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment

Introduction
Atrioventricular (AV) block, or heart block, is a cardiac conduction disorder where the electrical signals between the atria and ventricles are delayed or completely blocked. This disruption can significantly affect heart rhythm and overall cardiovascular health. As a leading heart clinic in Singapore committed to patient education and evidence-based care, we aim to provide a thorough, human-centred explanation of AV block.
What is Atrioventricular Block?
AV block is an impairment in the electrical conduction between the heart's atria and ventricles. Under normal circumstances, electrical impulses originate in the sinoatrial (SA) node and pass through the atrioventricular AV node to coordinate the heartbeat. These impulses are either delayed or wholly blocked in AV block, potentially causing various symptoms or serious health risks.
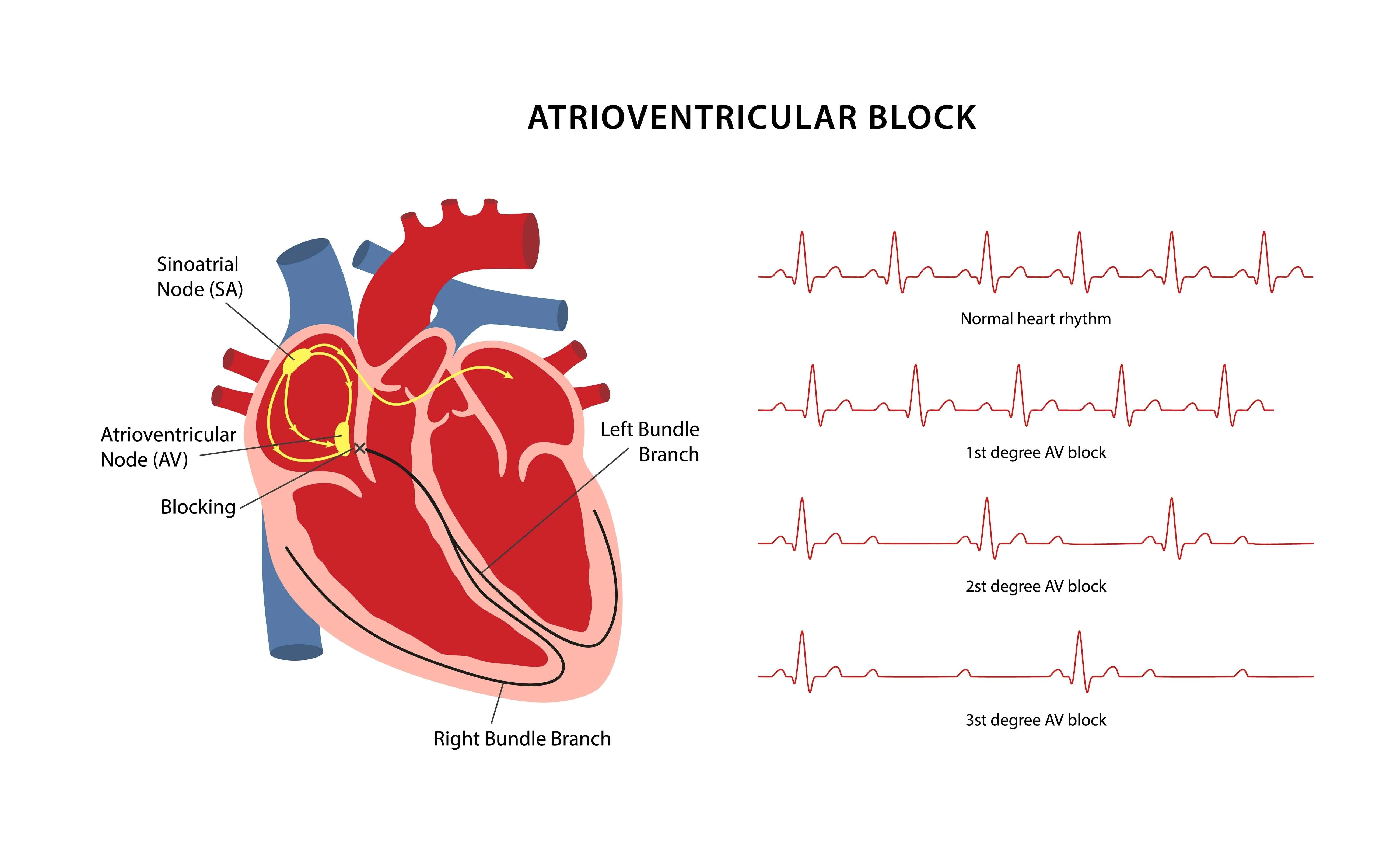

Types of Atrioventricular Block
First-Degree AV Block
The mildest form. Electrical signals are slowed but still reach the ventricles. Often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally.
Second-Degree AV Block
- Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach): Progressive delay of the AV signal until a beat is dropped.
- Mobitz Type II: More serious. Sudden dropped beats without prior signal delay. Can progress to complete heart block.
Expert Insight: Second-degree AV Block occurs when some of the electrical impulses from the upper chambers don't reach the lower chambers
Third-Degree (Complete) AV Block
A complete disconnection between atrial and ventricular electrical activity. The atria and ventricles beat independently. Requires urgent medical attention and often pacemaker insertion.
Causes and Risk Factors
Congenital Causes
- Born with AV block (rare)
- Associated with structural heart defects
Acquired Causes
- Ageing: Degeneration of conduction tissue
- Ischemic heart disease: Especially after myocardial infarction
- Cardiomyopathy: Heart muscle disease
- Infections: Lyme disease, rheumatic fever, endocarditis
- Surgery: Especially heart valve surgeries
- Medications:
- Beta-blockers:
- Calcium channel blockers
- Digoxin
- Antiarrhythmic drugs
Risk Factors
- Older age
- Existing heart disease
- Certain autoimmune conditions (e.g., lupus)
- Electrolyte imbalances
Symptoms of Atrioventricular Block
Symptoms depend on the degree of AV block. Many patients with first-degree AV block may remain asymptomatic.
Common Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
In third-degree AV block, symptoms can be severe and potentially life-threatening.
Symptom Detail: The Cleveland Clinic notes that symptoms of third-degree heart block are more intense due to the slow heart rate and can include nausea and fainting.
Complications of Untreated AV Block
- Heart failure
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Stroke due to embolism
- Reduced quality of life
- Increased risk of mortality in complete heart block
Diagnosing Atrioventricular Block
Physical Examination
- May reveal bradycardia
- Listening for an irregular heartbeat
- Checking for signs of reduced cardiac output
Diagnostic Tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): The primary tool to identify the type and severity of AV block.
- Holter Monitor: 24- to 48-hour ECG monitoring to catch intermittent AV blocks.
- Holter Monitor: Worn for weeks to capture irregular episodes.
- Echocardiogram: Assesses structural abnormalities.
- Electrophysiological Study (EPS): Advanced diagnostic for complex or unexplained cases.
- Blood Tests: Check for infections, electrolyte levels, or medication effects. .
Treatment Options for Atrioventricular Block
First-Degree AV Block
- Often does not require treatment
- Address underlying causes (e.g., adjust medications)
Second-Degree AV Block
- Mobitz Type I: Usually benign; monitor unless symptomatic
- Mobitz Type II:
- Often requires a pacemaker
- Treat underlying conditions
Third-Degree AV Block
- Requires immediate intervention
- A permanent pacemaker is the standard treatment
- Temporary pacing may be needed in emergencies
Pacemaker Therapy
Pacemakers help maintain a regular heart rhythm by delivering electrical impulses directly to the heart. There are various types:
- Single-chamber pacemakers (usually to the ventricle
- Dual-chamber pacemakers (to both the atrium and the ventricle)
- Biventricular pacemakers (used in heart failure with conduction delays)
- Expert Insight: The Cleveland Clinic explains that a permanent pacemaker is usually required for severe forms of heart block, such as third-degree block, to help the heart pump blood effectively.
Medications
Medications are not used to correct AV block, but may support heart function:
- Beta-blockers (used cautiously.
- ACE inhibitors.
- Diuretics (if heart failure is present).
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
The prognosis depends on the type of AV block and the presence of underlying conditions.
Favorable Prognosis
- First-degree AV block with no symptoms
- Mobitz Type I with normal cardiac function
Serious Prognosis
- Mobitz Type II or Third-Degree AV block
- Requires continuous monitoring and lifelong pacing in some cases
Follow-Up Care
- Regular pacemaker checks
- ECG monitoring
- Medication management
- Lifestyle changes


Living with Atrioventricular Block
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular cardiovascular exercise (under supervision)
- Low-sodium, heart-healthy diet
- Weight management
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco
Safety Considerations with a Pacemaker
- Avoid strong magnetic fields (e.g., MRI unless pacemaker-compatible)
- Inform security personnel at airports
- Carry a pacemaker identification card
Psychological Support
Living with a chronic condition can be emotionally taxing. Mental health support and cardiac rehabilitation programs can significantly improve quality of life.
Special Considerations
Pregnancy
Women with AV block can often have successful pregnancies with proper monitoring. Pacemaker implantation may be required before or during pregnancy, depending on the severity.
Athletes
Some athletes have first-degree AV block as a benign adaptation to intense training. However, evaluation is needed to distinguish benign forms from pathologic ones.
Pediatric AV Block
Congenital AV Block
- Rare but serious
- Detected prenatally or in early childhood
- May require early pacemaker implantation
Acquired AV Block in Children
- Often linked to infections or post-surgical complications
Expert Opinions and Clinical Guidelines
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association provide clear guidelines for diagnosing and managing AV block:
- Permanent pacing is the gold standard for high-grade blocks
- Early diagnosis can significantly reduce mortality and improve outcomes
Conclusion
Atrioventricular block is a condition with a broad spectrum of severity. While some cases are harmless and require minimal monitoring, others can be life-threatening without timely intervention. Our heart clinic prioritises early detection, patient-centred care, and advanced therapies such as pacemaker implantation to ensure the best outcomes
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with AV block or is experiencing symptoms suggestive of a heart rhythm disorder, book an appointment with our cardiologists. We're here to guide you every step toward better heart health.
This write-up has been medically reviewed by Dr. Michael Ross MacDonald, a consultant cardiologist at The Harley Street Heart & Vascular Centre in Singapore, to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.


