CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS TEST

Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test or CIMT test is a non-invasive ultrasound imaging technique used to measure the thickness of the carotid artery wall. It plays a crucial role in assessing the risk of cardiovascular disease by detecting the presence of atherosclerosis.
Introduction to the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test
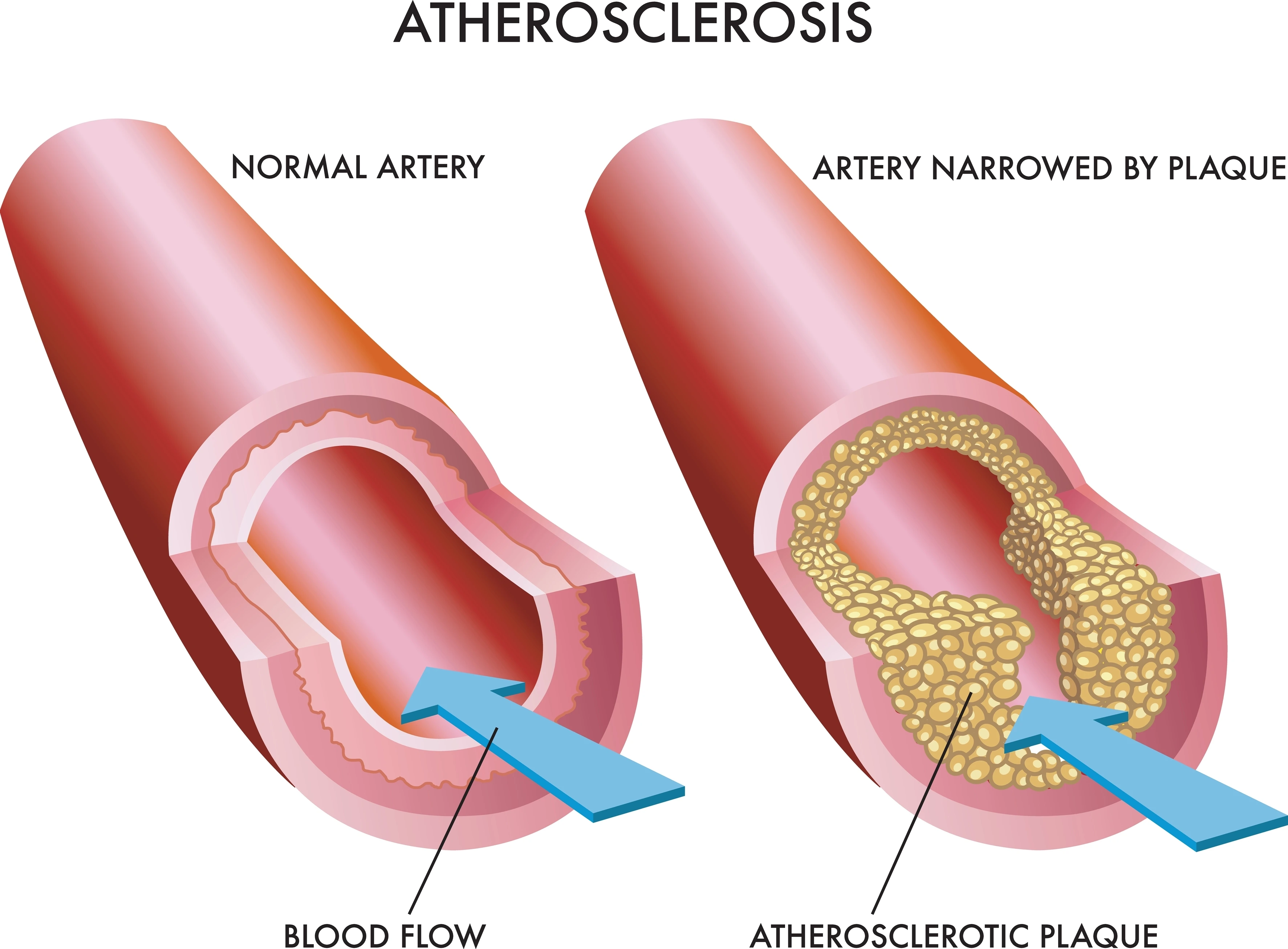
CIMT or Carotid-Intima Media Thickness test is used to diagnose the thickness of the carotid arteries' inner lining and middle layers. The CIMT test measures the combined thickness of the intima and media layers, which can provide valuable information about an individual's cardiovascular health. CIMT plays a crucial role in assessing cardiovascular diseases, as increased thickness in these artery walls or plaque buildup is an early indicator of atherosclerosis and can predict the risk of future cardiovascular events. CIMT testing typically involves using ultrasound imaging to measure the thickness of the carotid arteries, providing essential insights into an individual's risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
How the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test Works
This test is a non-invasive procedure used to measure the thickness of the inner two layers of the carotid artery. The principle behind CIMT measurement is that a thicker intima-media layer indicates atherosclerosis, a condition characterised by the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries. During the ultrasound imaging, a transducer is placed on the neck, emitting high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the artery walls. This produces images of the carotid artery, allowing doctors to measure the thickness of the intima-media layer. CIMT provides valuable information about arterial health, as it can detect the early stages of artery disease like asymptomatic atherosclerosis. By monitoring CIMT over time, cardiac doctors can assess the progression of the disease and make recommendations for preventive interventions like lifestyle changes or medication.
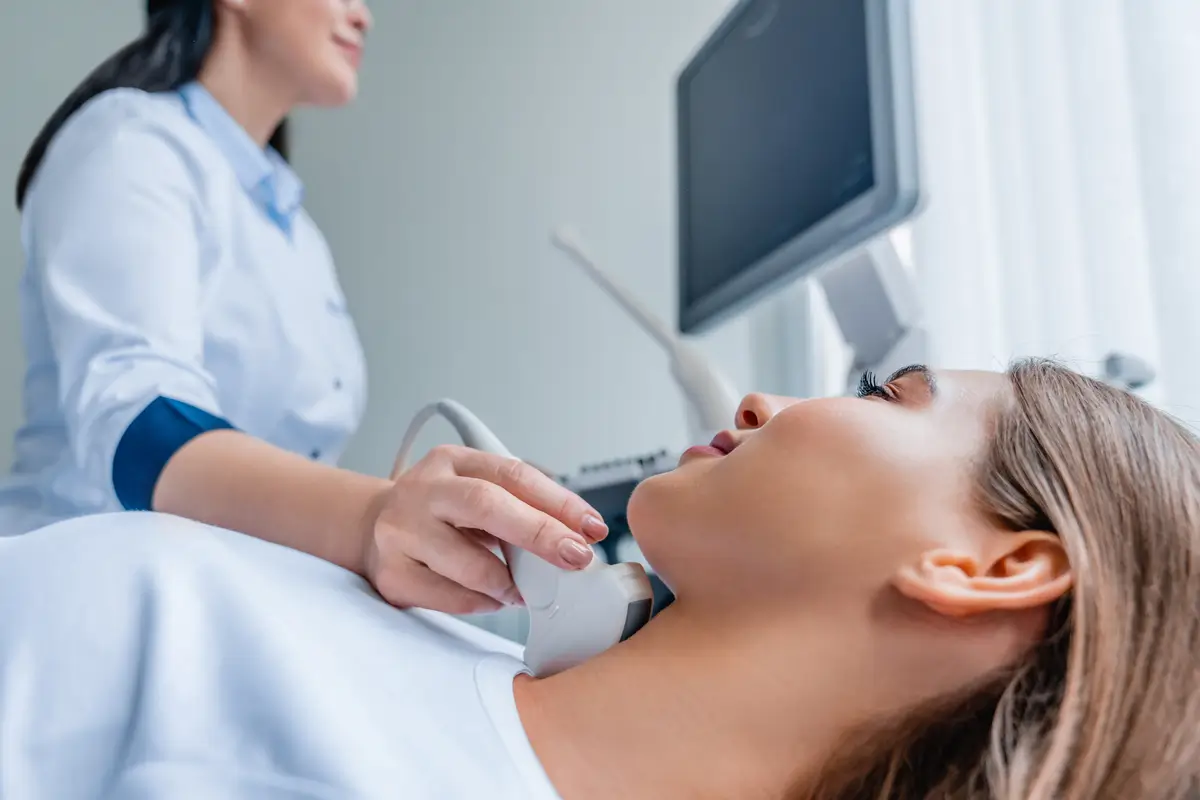
Who Should Consider a Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test is recommended for individuals with cardiovascular risk factors, such as smoking, high cholesterol levels, obesity, or a sedentary lifestyle. Additionally, those with a family history of heart disease should consider this test. Patients with diabetes or hypertension can also benefit from CIMT testing as these conditions increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis. The main goals of CIMT testing are the early detection of atherosclerosis and the monitoring of arterial health. By identifying the thickening of the carotid artery walls, this test helps cardiologists intervene before severe cardiovascular conditions develop.
Benefits of the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test offers several benefits to cardiovascular health. Firstly, it enables early detection of atherosclerosis, characterised by the thickening of arterial walls and a leading cause of heart disease. By identifying this condition in its initial stages, healthcare professionals can implement preventive measures to halt its progression and reduce the risk of serious cardiovascular events. Additionally, the CIMT test provides an accurate assessment of an individual's risk for cardiovascular disease, allowing for personalised prevention and treatment plans. Patients can significantly improve their cardiovascular health and overall well-being by tailoring interventions based on this assessment.
Preparing for a Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test
Are There Any Special Preparations Required Before the Test?
Specific preparatory measures should be taken before the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test. Firstly, the patient is instructed to fast for at least 8 hours before the test. They are also advised to avoid smoking and consuming caffeine-rich substances and alcohol.
It is advisable to wear comfortable clothing and avoid using any oils, lotions, or creams on the neck area on the day of the test. It is also essential to inform the healthcare professional about any existing medical conditions or medications to ensure accurate test results.
What Can I Expect During the CIMT Test?
During the CIMT test, you will be asked to lie down on an examination table. The healthcare professional will apply a clear gel to your neck area and use a handheld transducer to capture ultrasound images of the carotid arteries. The transducer emits sound waves, which bounce off the carotid arteries and create detailed images on a monitor.
How Long Does the CIMT Test Take?
The CIMT test usually takes around 30 to 60 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of the examination and the quality of the images required. It is a relatively quick and painless procedure, and patients can resume their normal activities immediately after the test.
Post-Test Care and Follow-up
Specific post-test care and follow-up steps are essential after a Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test. Immediate post-test observations should be made to identify any complications or side effects. Once the test results are obtained, they should be thoroughly discussed with the patient, emphasising any areas of concern or abnormalities. Lifestyle modifications, such as changes in diet and exercise, should be recommended to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Medication management may also be necessary to address any underlying health conditions. Regular follow-up assessments should be scheduled to monitor the patient's progress and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Costs of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test In Singapore
In Singapore, the cost of a Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test can vary from $300 - $800 depending on several factors. Insurance considerations play a crucial role in determining the out-of-pocket expenses for patients. The costs associated with the CIMT test include medical service fees, diagnostic equipment fees, and additional charges for interpretation and analysis. Individuals must understand and consider these costs before the test to plan their finances accordingly.
Conclusion
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test is essential for assessing cardiovascular health. Measuring the carotid artery walls' thickness can identify early signs of atherosclerosis and potential cardiovascular disease. This significant test allows healthcare professionals to identify at-risk individuals and promptly initiate preventive measures. Ultimately, CIMT testing encourages individuals to proactively assess their cardiovascular health and take necessary steps to maintain a healthy heart.
Frequently Asked Questions About Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test
Is the CIMT Test Painful?
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test is typically not painful. It involves using ultrasound to measure the thickness of the inner layers of the carotid artery walls. While you may feel a slight pressure on your neck as the ultrasound probe moves around, it is generally painless.
Who Should Consider CIMT Testing?
Individuals who should consider the carotid intima-media thickness testing are at risk for cardiovascular disease. This includes people with a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes. It is also recommended for those who smoke, are overweight, or have a sedentary lifestyle. This non-invasive test can help identify early signs of atherosclerosis and determine the need for further intervention or lifestyle changes.
How Often Should CIMT Be Repeated?
The frequency of repeating the carotid intima-media thickness test depends on factors such as the patient's age, risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and previous test results. In general, it is recommended to repeat the test every 1 to 3 years for individuals with average results and no additional risk factors. However, for those with abnormal results or higher risk, more frequent testing may be necessary to monitor changes in the artery walls.
How Do You Measure Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness?
Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) can be measured using ultrasound imaging. A high-resolution ultrasound probe is placed on the neck to capture images of the carotid arteries. The CIMT is then measured using specialised software that quantifies the thickness of the innermost layer (intima) and the middle layer (media) of the carotid artery walls. This measurement can help assess the presence and severity of atherosclerosis, which is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What Is the Difference Between a Carotid Ultrasound and a CIMT Test?
A carotid ultrasound test uses sound waves to produce images of the carotid arteries in the neck. It is primarily used to assess the presence or extent of blockages or narrowing in these arteries, which can increase the risk of stroke. On the other hand, a CIMT (Carotid Intima-Media Thickness) test measures the thickness of the inner two layers of the carotid artery walls. It helps to evaluate the overall health and condition of the arteries and can indicate the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
How Accurate Is a CIMT Test?
A carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) test is a non-invasive ultrasound procedure used to assess the thickness of the carotid artery walls. It is considered a reliable tool for detecting early stages of atherosclerosis.