Coronary Angiogram: Your Complete Guide
A coronary angiogram is a test which allows your cardiologist to visualise the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries supply the heart muscle with blood and oxygen. The procedure can be done from the wrist (radial artery) or the leg (femoral artery).
Proceed to book an appointment for a coronary angiogram with one of the best cardiologists in Singapore or contact us for further details to schedule your cardiac consultation.

What is a Coronary Angiogram?
Definition of Coronary Angiogram
A coronary angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure used to study the coronary arteries. It involves using a catheter to inject contrast dye and obtain X-ray images, enabling cardiologists to diagnose and treat heart-related issues.
The procedure of a Coronary Angiogram
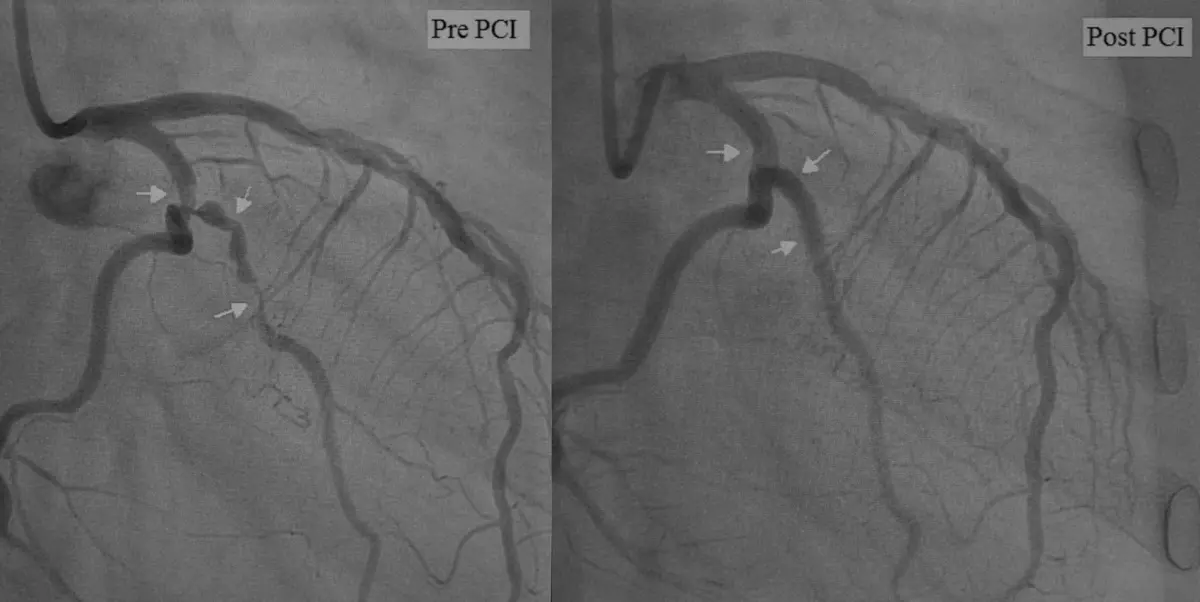
A coronary angiogram is a specific type of coronary angiography conducted to examine the blood flow through the coronary arteries meticulously. This essential diagnostic procedure helps in identifying any blockages or narrowings that may be present. Based on the findings, appropriate interventions, such as stenting or angioplasty, may be given. This process is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of vascular issues, ensuring that timely and effective treatment can be administered to maintain heart health.
How Coronary Angiogram Diagnoses Heart Conditions
This procedure helps diagnose coronary artery disease and determines suitable treatment plans for patients with cardiac issues.
Importance of Coronary Angiogram in Identifying Coronary Artery Disease
A coronary angiogram is an essential diagnostic tool for identifying and assessing coronary artery disease, guiding the cardiologist in devising a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
Coronary Angiogram as a Minimally Invasive Diagnostic Test
As a minimally invasive procedure, a coronary angiogram allows for thoroughly examining coronary arteries without major surgeries, providing accurate insights into the patient's heart health.
What to Expect During a Coronary Angiogram?
Risks and Complications of a Coronary Angiogram
Before the procedure, thorough preparation and assessment are conducted to minimise potential risks and complications associated with coronary angiogram, ensuring patient safety.
Preparation for Coronary Angiogram
Patient preparation involves a detailed medical history review, a discussion of risks and benefits, and the administration of local anaesthetic at the catheter insertion site to ensure patient comfort. Also, a coronary angiogram requires you to fast for at least 6 hours and can be done as a day-case procedure.
Steps Involved in the Coronary Angiogram Procedure
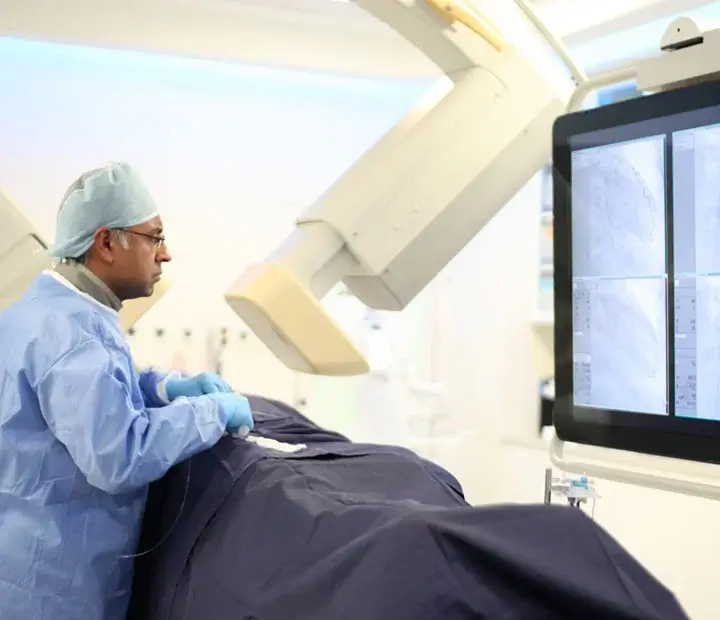
During the procedure, a catheter is carefully inserted through the wrist or groin, reaching the coronary arteries, and contrast dye is injected to obtain X-ray images for diagnosis. During an angiogram, patients are continually linked to a heart monitor (ECG) that shows the heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure. The procedure usually takes 10-20 minutes.
Use of Dye and X-ray Imaging in Coronary Angiogram
Using a radio-opaque dye (usually iodine-based) and X-ray imaging provides cardiologists with clear visualisation of the coronary arteries, enabling them to detect any abnormalities or blockages in the blood vessels.
Recovery and Discharge Process After Coronary Angiogram
Following the procedure, patients are monitored briefly before discharge to go home the same day, allowing for a smooth recovery process.
Understanding the Role of a Cardiologist in Coronary Angiogram
Responsibilities of a Cardiologist in Performing Coronary Angiogram
Cardiologists play a critical role in performing and interpreting coronary angiograms, using their expertise to diagnose and devise suitable treatment plans for patients with heart conditions.
Cardiologist’s Contribution to Diagnosing Heart Conditions
Through their in-depth understanding of the cardiovascular system, cardiologists utilise coronary angiograms as a diagnostic tool to identify and address various heart conditions.
Collaboration with Cardiologist for Coronary Artery Treatments
Cardiologists work closely with patients, explaining the results of the coronary angiogram and discussing potential treatment options, including stenting, angioplasty, or coronary artery bypass grafting.
When to Consult a Cardiologist for a Coronary Angiogram
Patients should seek the expertise of a cardiologist when experiencing symptoms of coronary heart disease, as early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for favourable outcomes.
Ensuring Cardiologist’s Expertise in Coronary Angiogram Procedure
Choosing a qualified and experienced cardiologist for the coronary angiogram procedure is vital, ensuring a thorough and accurate assessment of the patient’s heart health.
Potential Complications and Risks of Coronary Angiogram
Identifying Risks Associated with Coronary Angiogram
Understanding the potential risks associated with coronary angiograms supports informed decision-making and enables medical professionals to provide appropriate care and monitoring during and after the procedure.
Understanding Complications Arising from Coronary Angiogram
Potential complications of coronary angiogram, while rare, include allergic reactions to the contrast dye, blood vessel injury, and heart rhythm irregularities, which are closely monitored and managed by healthcare providers.
Steps to Minimise Risks and Complications During the Procedure
Medical teams take stringent measures to minimise the risks associated with coronary angiograms, ensuring patient safety and well-being throughout the entire procedure.
Post-procedural Management of Complications from Coronary Angiogram
Following a coronary angiogram, healthcare professionals carefully monitor patients for any post-procedural complications and provide appropriate management if necessary, addressing any concerns effectively.
Addressing Patient Concerns and Anxiety Regarding Risks
Patients are encouraged to openly discuss any concerns or anxieties regarding potential risks with their healthcare provider, fostering a supportive and transparent patient-doctor relationship.
Coronary Angiogram as a Diagnostic Tool for Heart Conditions
Study of Coronary Arteries and Blood Flow through Angiogram
By visualising blood flow and blockages in the coronary arteries, coronary angiogram provides crucial information for cardiologists to develop tailored treatment plans.
Comparison of Coronary Angiogram with Other Heart Diagnostic Tests
Compared to other heart diagnostic tests, coronary angiogram offers detailed insights into the condition of the coronary arteries, making it an indispensable tool for identifying and treating heart-related issues.
Role of Coronary Angiogram in Determining Suitable Treatment Plans
Based on the findings from coronary angiograms, cardiologists can determine the most suitable treatment approach, which may include medical management, angioplasty, stenting, or coronary artery bypass grafting.
Interpretation and Analysis of Findings from Coronary Angiogram
Cardiologists carefully analyse the coronary angiogram results, translating the findings into comprehensive reports that guide the ongoing management and treatment of the patient’s heart condition.
Conclusion
Book a teleconsultation or schedule an appointment with one of our cardiologists for a Coronary Angiogram to test your heart's health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Coronary Angiogram
What Is a Coronary Angiogram?
A coronary angiogram is a procedure that uses a special dye and X-rays to see how blood flows through the coronary arteries of the heart.
How Is a Coronary Angiogram Done?
During a coronary angiogram, a thin, flexible plastic tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel in the arm or groin and threaded into the heart's coronary arteries. The dye is then injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken to show the blood flow in the heart.
What Can a Coronary Angiogram Show?
A coronary angiogram can help your doctor see if the coronary arteries are narrowed, if there are any blockages, and the overall blood flow to the heart muscle. This information helps in diagnosing and planning treatment for heart conditions.
Is a Coronary Angiogram a Risky Procedure?
While a coronary angiogram is considered a minimally invasive procedure, there is a risk of complications such as bleeding, damage to blood vessels, or allergic reactions to the dye used. Your healthcare team will discuss the potential risks and benefits with you before the procedure.
What Is the Recovery Like After a Coronary Angiogram?
After the procedure, you must lie still for a few hours to allow the catheter insertion site to heal. You may be instructed to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a short period. Most patients are able to go home the same day of their procedure.
Can a Coronary Angiogram Lead To Further Treatment?
Yes, blockages or narrowings are discovered during the angiogram. In that case, your doctor may perform additional procedures such as coronary angioplasty (using a balloon to widen the artery) or placing a stent (a small mesh tube) to help keep the artery open.
What Should I Expect During a Coronary Angiogram?
During the procedure, you will be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie on your back on a special X-ray table in the catheter lab room. Your healthcare team will be on hand to help and support you throughout the process.
Is a Coronary Angiogram Painful?
You may feel discomfort or pressure when the catheter is inserted, but your healthcare team will take steps to minimise pain or discomfort. Some patients may also experience a warm sensation when the dye is injected.
How Long Does a Coronary Angiogram Take?
The actual angiogram procedure can take anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour. However, it would help if you planned for additional time for preparation, recovery, and any potential follow-up discussions with your doctor.
Can I Wear Contact Lenses During a Coronary Angiogram?
It is recommended to avoid wearing contact lenses during the procedure, as you may need to lie flat for an extended period. Your healthcare team can provide further guidance on any specific requirements related to contact lenses or other personal items.