TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAM (TTE) in Singapore
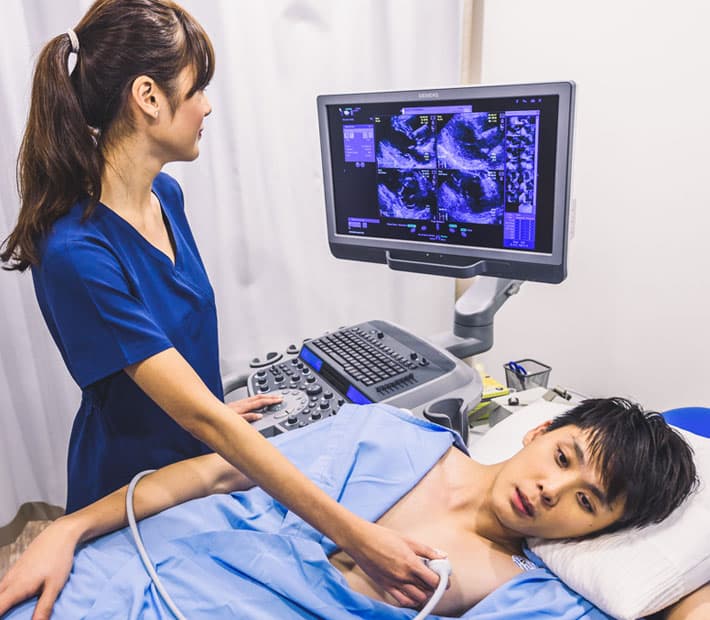

Transthoracic Echocardiogram is a common type of echocardiogram that is used to assess the structure and function of the heart. It is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart and the blood flow within it, employing techniques such as Doppler and colour Doppler to enhance visualisation.
In Singapore, the TTE test is widely available and can be done at hospitals and specialised cardiology clinics such as The Harley Street Heart and Vascular Centre. In fact, you may even proceed to book an appointment for a medical consultation with one of our cardiologists or contact us for further details to schedule your TTE test.
What is Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is a type of echocardiography that involves the use of a transducer placed on the left side of the chest wall to obtain images of the heart. It is a painless procedure that allows doctors to evaluate the size and function of the heart chambers, assess the movement of the heart walls, and examine the heart valves and blood vessels. TTE is also commonly referred to as a standard transthoracic echocardiogram.
An echocardiogram monitor is part of the setup, displaying real-time images as the echocardiogram is done. This procedure is crucial for detecting heart problems, as it can visualise the electrical activity and overall function of different parts of the heart.
What Is the Purpose of Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
The purpose of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is to provide detailed information about the structure and function of the heart. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor various heart conditions such as congenital heart disease, heart failure, and problems with the heart valves or the heart muscle. TTE is used to assess the overall health of the heart and can also be used to guide treatment decisions.
How Long Does a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Test Take?
A Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test usually takes around 30 to 60 minutes to complete. The actual transthoracic echocardiography procedure itself may only take a few minutes, but the sonographer may need to capture different views of the heart from different angles to obtain a comprehensive assessment. The length of the test can vary depending on the individual and the complexity of the heart condition being evaluated.
Where Can I Take The Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Test In Singapore?
In Singapore, the Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test can be taken at various medical facilities, including hospitals, and cardiac clinics. It is important to consult with your doctor to determine the most appropriate location for your TTE test based on your specific needs and medical history.
How Much Does a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Test Cost In Singapore?
The cost of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test in Singapore can vary depending on the facility where the test is performed. On average, the cost can range from SGD $400 to SGD $1,000. It is advisable to check with your healthcare provider or insurance company for specific cost details and coverage options.
Why Is Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Performed?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is performed to help diagnose and monitor various heart conditions. It provides valuable information about the structure and function of the heart, allowing doctors to assess the overall health of the heart and identify any abnormalities. TTE can help diagnose conditions such as heart valve problems, congenital heart disease, heart failure, and abnormalities in the heart muscle. If your doctor suspects you might have heart problems, a Doppler echocardiography could be recommended as part of your TTE to get a closer look at the blood flow through your heart.
What Conditions Can Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Help Diagnose?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) can help diagnose a wide range of heart conditions. It is particularly useful in assessing heart valve problems, such as valve regurgitation or stenosis. TTE can also detect congenital heart disease, which is a condition that is present at birth and can help evaluate the severity of heart failure and determine the underlying cause. Additionally, TTE can identify abnormalities in the heart muscle and detect any issues with the blood flow within the heart.
What Are the Benefits of Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Over Other Tests?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) offers several benefits over other types of tests used to assess heart health. It is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve radiation exposure, making it safe for individuals of all ages, including pregnant women. TTE provides real-time images of the heart, allowing doctors to assess the heart's structure and function immediately. It is also a widely available and cost-effective test that can be performed in a variety of healthcare settings.
Are There Any Risks or Side Effects Associated With Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is considered a safe and well-tolerated procedure. It does not involve the use of ionising radiation, which makes it a low-risk test. There are no known long-term side effects associated with TTE. However, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or irritation from the electrode or the gel used during the procedure. In rare cases, a small number of people may have an allergic reaction to the gel.
How to Prepare for a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Test?
What Should I Avoid Before the Test?
Before a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, it is advisable to avoid eating a heavy meal or drinking caffeine for a few hours. Consumption of alcohol must be avoided at least 24 hours before the test. These can affect your heart rate and may interfere with the test results. It is important to follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding food and drink restrictions.
What Should I Wear During the Test?
For a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, you may be asked to remove your clothing from the waist up and wear a hospital gown. It is important to wear loose-fitting clothing that is easy to remove and put back on. This will allow the sonographer to easily access your chest and obtain clear images of your heart.
Do I Need to Stop Any Medications Before the Test?
If you are taking any medications, it is important to consult with your doctor before a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test. In most cases, you can continue taking your medications as prescribed. However, certain medications may affect your heart rate or blood pressure, which can interfere with the test results. Your doctor will advise you if any changes to your medication regimen are necessary.
What to Expect During a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) Test?
What Will the Technician Do During the Test?
During a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, a trained technician called a sonographer will perform the procedure. The sonographer will apply a gel to your chest to improve the contact between your skin and the transducer. The transducer, which is a small handheld device, will be moved around your chest to obtain different views of the heart. The sonographer may ask you to change positions or hold your breath at certain times to obtain better images.
What Should I Do During the Test?
During a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, it is important to remain still and relaxed. The sonographer will provide instructions on when to hold your breath or change positions. It is important to follow these instructions to ensure the quality of the images captured. You may feel slight pressure or mild discomfort from the transducer, but the overall procedure should not cause any significant pain.
Will the Test Be Painful or Uncomfortable?
A Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test is generally not painful. The gel applied to your chest may feel slightly cool or wet, and the pressure from the transducer may cause some mild discomfort. However, the transthoracic echocardiography procedure is typically well-tolerated and should not cause any significant pain. If you experience any discomfort during the test, it is important to communicate with the sonographer.
Understanding the TTE Test Results
After a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, the images obtained will be reviewed by a cardiologist, who will interpret the results. The test results will provide information about the structure and function of the heart, allowing the cardiologist to assess its overall health. The results can help determine if the heart is functioning normally or if further testing or treatment is required.
What Does It Mean if the Test Results Are Normal?
If the test results of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) are normal, it means that there are no significant abnormalities in the structure or function of the heart. This indicates a healthy heart and no immediate cause for concern. However, it is important to note that a normal TTE does not guarantee the absence of any underlying heart conditions, as some conditions may not be detectable with this test alone.
What Does It Mean if the Test Results Are Abnormal?
If the test results of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) are abnormal, it means that there are some abnormalities or irregularities in the structure or function of the heart. The exact meaning of the abnormalities will depend on the specific findings. The cardiologist will carefully evaluate the results and determine the significance of the abnormalities and the necessary course of action.
Will I Need Further Testing if the Results Are Abnormal?
If the test results of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) are abnormal, further testing may be required to confirm the findings and provide more detailed information. Additional tests, such as a Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) or a stress echocardiogram, may be recommended to obtain a more comprehensive assessment of the heart's structure and function. The cardiologist will discuss the next steps and any necessary follow-up testing or treatment options with you.
Frequently Asked Questions About TTE
What Is the Difference Between a Transthoracic Echo and a Regular Echo?
A Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is a type of echocardiogram that is performed by placing a transducer on the chest wall to obtain images of the heart. This is the most common type of echocardiogram and is often referred to simply as an echocardiogram. A regular echo may refer to any type of echocardiogram, including TTE, Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE), or stress echocardiogram.
What Are the Side Effects of a Transthoracic Echocardiogram?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is generally a safe and well-tolerated procedure with minimal side effects. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort or irritation from the transducer or the gel used during the transthoracic echocardiography procedure. In rare cases, a small number of people may have an allergic reaction to the gel. It is important to inform the sonographer if you have any allergies or sensitivities.
Why do I need a transthoracic echocardiogram?
A Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is needed to closely examine your heart's structure and function. It's especially useful for diagnosing heart issues, assessing damage after a heart attack, or monitoring heart conditions. This test helps doctors make informed decisions about your heart health.
Can I Eat Before a Transthoracic Echocardiogram?
Prior to a Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) test, it is advisable to avoid eating a heavy meal or drinking caffeine for a few hours. This is because food and caffeine can affect your heart rate and may interfere with the test results. Alcohol must be avoided as well. It is important to follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding food and drink restrictions.
What to expect at an echocardiogram for a woman?
During an echocardiogram for a woman, expect a simple, non-invasive procedure. You'll lie on an examination table, and a technician will apply a special gel to your chest. An ultrasound device is moved over the chest to create heart images. The process is painless, takes about 30-60 minutes, and respects privacy.
What is a transesophageal echocardiogram?
A transesophageal echocardiogram is a medical test where a small probe is inserted down the throat to take close-up images of the heart. This method provides detailed pictures, helping doctors assess heart health more accurately than standard echocardiograms. It's often used when clearer images are needed.
How Accurate Is Transthoracic Echocardiogram?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) is a highly accurate test for evaluating the structure and function of the heart. It provides detailed images and measurements that allow doctors to assess the health of the heart and identify any abnormalities. However, it is important to note that TTE is just one part of the diagnostic process, and the accuracy of the test results also depends on the skill and expertise of the sonographer and the interpreting cardiologist.
Does Transthoracic Echocardiogram Show Blockages?
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) can provide valuable information about the structure and function of the heart, including the presence of any blockages in the blood vessels. However, it is not the primary test used to diagnose blockages in the blood vessels. If blockages are suspected, further testing such as a stress test, cardiac catheterization, or a computed tomography angiogram (CTA) may be recommended to evaluate the blood flow and assess the presence of blockages.
Conclusion
Overall, transthoracic echocardiogram is an important tool in the diagnosis and management of cardiac conditions. Its non-invasive nature, ability to assess both structure and function and widespread availability make it a valuable diagnostic tool for cardiologists around the world..


