EXERCISE TREADMILL TEST (ETT)
An exercise treadmill test (ETT) which is also generally known as an exercise stress test provides the cardiologist with general information about how well the heart copes with exercise and may detect an underlying problem that is not present on the resting ECG. As the body works harder during exercise, the working muscles require more oxygen, so the heart must pump more blood. The exercise test result can show if there is a reduction in blood supply to the heart or if any abnormal heart rhythms develop with exercise.
You may proceed to book an appointment for a consultation with one of the best cardiologists in Singapore or contact us for further details.
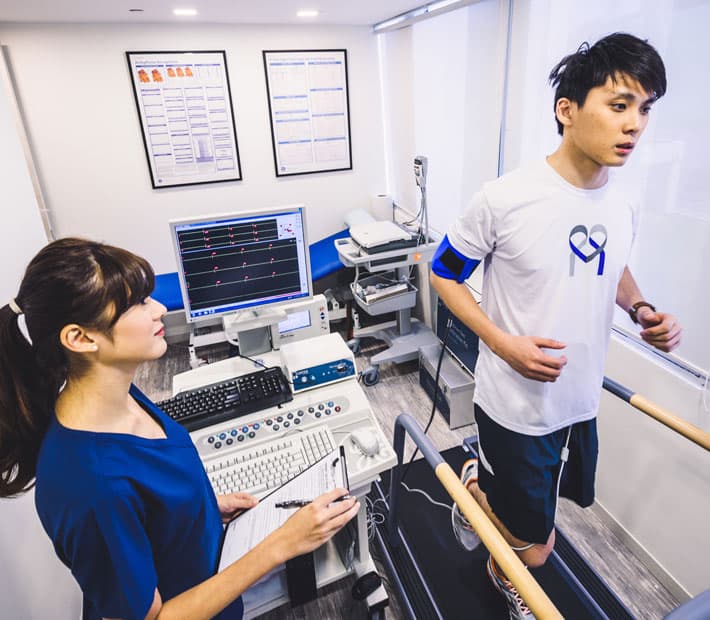

What Is an Exercise Treadmill Test?
What Is Meant by Stress Testing?
Stress testing is a test that is done to measure how well your heart works during physical activity. It typically involves some form of exercise, whether it's walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike, while your heart rate and blood flow are monitored.
What Is a Treadmill?
A treadmill is a machine used for walking, running, or climbing while remaining in one place. In an Exercise Treadmill Test, you will be asked to walk on a treadmill at an increasing speed and incline to increase the stress on your heart.
How Is an Exercise Treadmill Test Performed?
According to Dr. Michael Ross MacDonald, during an exercise treadmill test, the ECG electrodes are attached to the patient and the readings are constantly displayed on the treadmill monitor. The blood pressure is also recorded every 2-3 minutes. The treadmill starts slowly and the speed and its slope are increased every three minutes according to a standard protocol. The treadmill test is stopped when the patient achieves a target heart rate or if the patient develops symptoms, such as chest discomfort, breathlessness or dizziness. The test may also be stopped if there are significant changes in the ECG or if blood pressure falls significantly as this should normally increase with exercise.
Why Is an Exercise Stress Test Recommended?
What Is the Role of Exercise Stress Tests in Detecting Heart Disease?
The primary role of any exercise stress test such as the ETT is to detect heart disease. During the test, your cardiologist will be looking for signs of coronary artery disease or other heart conditions by monitoring your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG readings. An abnormal ETT result may indicate blockages in your coronary arteries or other issues with your heart function or blood flow.
How Is ETT Beneficial in Assessing the Risk of Heart Disease?
ETT is also beneficial in assessing the risk of heart disease, particularly in individuals who may be at risk due to factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, or a family history of heart disease. Your cardiologist may recommend an ETT to assess your overall cardiac health and determine if you are at increased risk for heart disease.
What Is the Significance of ETT for Those Who Have Already Been Diagnosed With Heart Disease?
For those who have already been diagnosed with heart disease, an ETT can be a valuable tool for monitoring their condition and determining the effectiveness of their treatment plan. ETT can help assess their heart function and evaluate if their treatment is helping to manage their heart disease.
What Are the Components of an ETT?
What Is the Role of Electrocardiogram (ECG) In ETT?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is an important component of an ETT. It measures the electrical activity of your heart during exercise and helps to identify any areas of your heart that may not be getting enough oxygen due to reduced blood flow.
What Is The Role of Echocardiogram Stress Test In ETT?
The role of an echocardiogram such as a 2D echocardiography in ETT is to provide a more detailed assessment of the heart's function during exercise. ETT can detect abnormal heart rhythms and blood flow, but an echocardiogram can show structural abnormalities and how the heart responds to stress. This additional information is useful for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular disease.
What Is the Role of the Nuclear Stress Test in ETT?
A nuclear stress test is another imaging test that is sometimes used during an ETT. It involves administering a small amount of a radioactive substance such as dobutamine to help visualize blood flow to your heart muscle. This test is called dobutamine stress echocardiogram (DSE) and can help your cardiologist identify the presence of any blockages in your arteries.
How Is Heart Rate Monitored During ETT?
Heart rate is monitored during an ETT using a cardiac stress test. The test may involve walking on a treadmill or pedalling on a stationary bike while your heart rate and other vital signs are monitored.
What Are the Risks of an ETT?
Is There a Possibility of Developing Coronary Artery Disease Due to ETT?
There is no evidence to suggest that ETT can cause coronary artery disease. However, the test may exacerbate existing heart conditions in some patients, particularly those who have significant blockages in their arteries.
What Should Be Done in Case of an Abnormal ETT Result?
If you receive an abnormal ETT result, your cardiologist may recommend further testing or treatment to address any issues with your heart function or blood flow. They may also suggest lifestyle changes or medication to help manage your risk factors for heart disease.
Can ETT Lead to Heart Failure or Abnormal Heart Rhythm?
While ETT or any exercise stress test is generally considered safe, there is a small risk of developing heart failure or an abnormal heart rhythm during the test. Your cardiologist will closely monitor you during the test to ensure your safety.
When Should I Consult a Cardiologist for ETT?
What Are the Warning Signs Indicating the Necessity of ETT?
You should consult a cardiologist for ETT if you have any warning signs of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness during exercise. If you have a family history of heart disease or have any risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol, your cardiologist may also recommend a stress test.
What Precautions Should Be Taken Before, During, and After the ETT?
Before your ETT, you should avoid eating or drinking for several hours to ensure accurate results. You should also wear comfortable clothing and shoes suitable for exercise. During the test, you should alert your cardiologist if you experience any symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness. After the test, you may resume your normal activities as usual.
When Should I Stop the Test During ETT?
You should stop the stress test if you experience any symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness. Your cardiologist may also stop the test if they observe any irregularities in your heart function or blood pressure.
An exercise treadmill test is a valuable tool for assessing cardiac health and detecting heart disease. If you have any concerns about your heart health or are at increased risk for heart disease, consult a cardiologist to see if an ETT or other exercise stress test may be right for you.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Exercise Treadmill Test
Some frequently asked questions regarding exercise treadmill tests include the purpose of the stress test, how to prepare for it, and what to expect during the test. Other common questions include the duration of the test, whether or not medications can be taken prior to the test, and what the results of the test mean for overall health and fitness. As always, it's important to discuss any concerns or questions with a reputable healthcare provider such as the cardiologists available at The Harley Street Heart & Vascular Centre.
What Is a Good Result on a Treadmill Stress Test?
A good result on a treadmill stress test depends on several factors, including age, fitness level, and medical history. Generally, a good result indicates that the heart is functioning well during exercise and that there are no signs of significant blockages in the arteries. Results are often measured in METs (metabolic equivalents) and a score of 9 or higher is considered a good result. However, it's important to note that results can vary for each individual and should be evaluated by a medical professional.
How Do I Pass My Exercise Treadmill Test?
To pass an exercise treadmill test, it's important to properly warm up, wear appropriate clothing and shoes, maintain correct running form, and stay focused on your breathing and pace. Gradually increasing the speed and incline throughout the test can also help show improvement in cardiovascular endurance. Make sure to hydrate properly before, during, and after the test to avoid exhaustion.
What Is the Exercise Treadmill Test For?
The exercise treadmill test is typically used to evaluate the function and health of the heart and lungs. During the test, a person will walk or run on a treadmill, with the intensity gradually increasing until they reach their maximum heart rate. The test can help identify any underlying cardiovascular or respiratory issues, as well as assess physical fitness levels. It is often used as a diagnostic tool for certain heart conditions or to monitor treatment effectiveness.
What Does a Positive Treadmill Test Mean?
A positive treadmill test means that during exercise or physical activity on the treadmill, a person's heart rate and blood pressure are monitored and reveal evidence of underlying heart disease or blockages. This could include symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, abnormal heart rhythms, or changes in blood pressure. Further testing and evaluation by a healthcare professional may be necessary to determine the extent of heart disease and appropriate treatment options.
What Is a Normal Treadmil Score?
A normal treadmill score is around 5 to 10. This score is based on the metabolic equivalent, or MET, which is a measure of the amount of energy used during physical activity. A higher score is indicative of better cardiovascular health and fitness levels. However, the normal range can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, and physical condition. It's best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine what is a normal treadmill score for you. According to the National Library of Medicine, the MET score can be categorized as follows: less than 5 METS is considered poor, 5–8 METS is classified as fair, 9–11 METS is regarded as good, and 12 METS or more is considered excellent.
How Long Is an Exercise Treadmill Test?
An exercise treadmill stress test typically lasts between 30 minutes to one hour, depending on the individual's heart rate response and physical endurance. The test begins with a gradual increase in intensity on a treadmill, and the goal is to reach a target heart rate while monitoring blood pressure and EKG readings. The length of the test can vary based on the individual's physical fitness and ability to tolerate the exertion.
What Not to Do Before an Exercise Treadmill Test?
Before a stress test, avoid eating or drinking anything except for water for at least three hours prior to the test. Also, avoid caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and strenuous exercise for at least 24 hours before the test. It is important to follow these instructions to ensure accurate results during the stress test.