PERMANENT PACEMAKER INSERTION

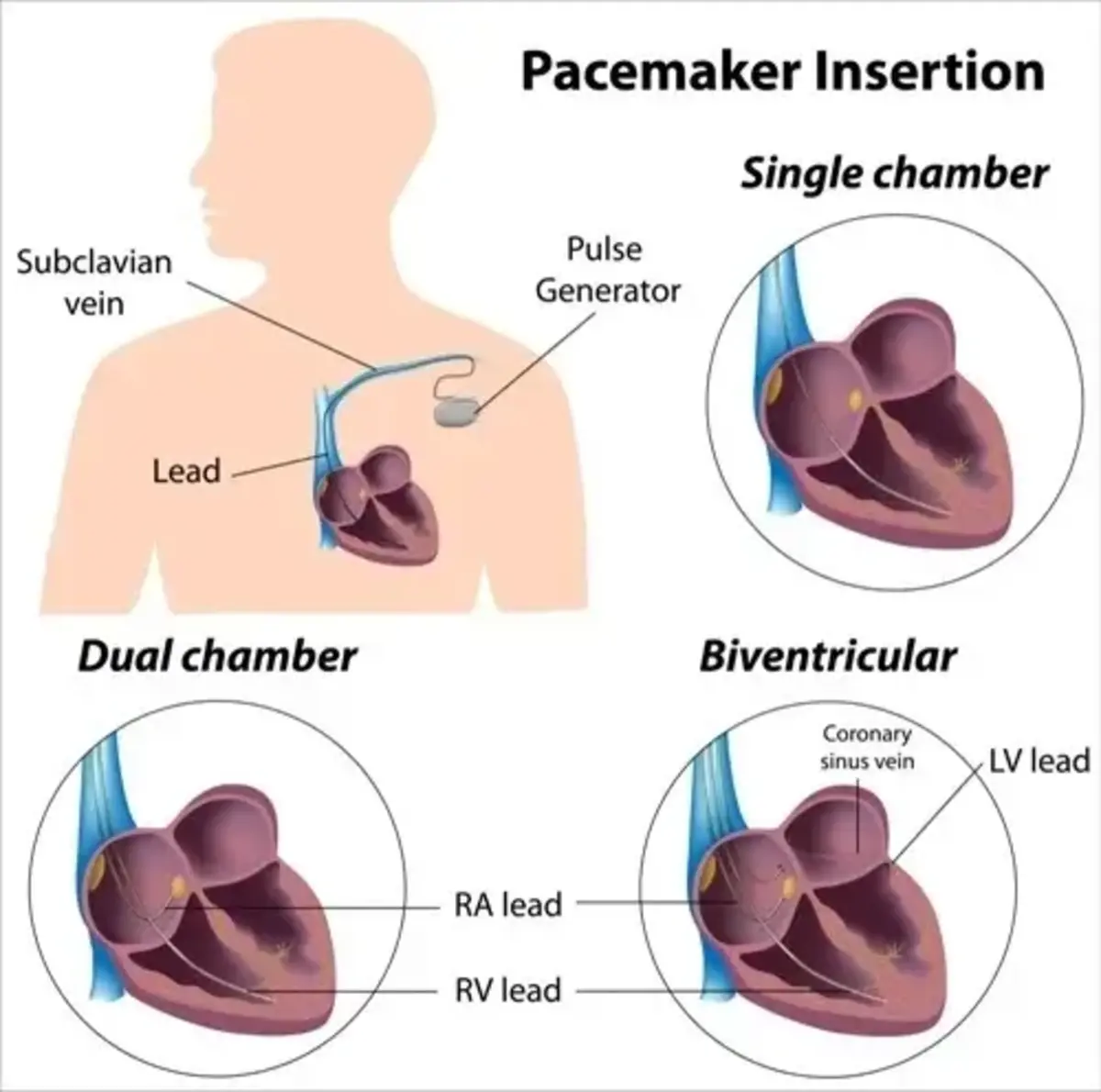
A Permanent Pacemaker is a small electronic device, about the size of a matchbox, inserted beneath the skin (usually below the left or right collar bone) and connects to the heart via one or more electrical wires (pacemaker leads) passed inside blood vessels.
The Permanent Pacemaker (PPM) Insertion procedure is usually performed by the cardiologist using a local anaesthetic and light sedation and takes about one to two hours. Inserting a permanent pacemaker becomes essential when the heart's natural electrical system is not functioning properly, leading to irregular heartbeats and related symptoms.

What Is a Permanent Pacemaker Insertion?
Indications for Permanent Pacemaker Insertion
Patients may require a permanent pacemaker for various cardiac conditions, including heart block, heart failure, and other heart rhythm disturbances. The decision for pacemaker implantation is made after a thorough evaluation by a cardiac specialist and a proper assessment of the patient's medical history.
The Role of a Permanent Pacemaker in Managing Heart Rhythm Abnormalities
A permanent pacemaker plays a crucial role in ensuring that the heart maintains a consistent and appropriate rhythm, thus preventing symptoms associated with irregular heartbeats, such as dizziness, fainting, and shortness of breath.
Types of Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Procedures
Different permanent pacemaker implantation procedures exist, including single-chamber, dual-chamber, and cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) pacemakers. The choice of pacemaker type depends on the specific cardiac condition and individual patient needs.
How Does a Pacemaker Generator Work?
The pacemaker generator is programmed to monitor the heart's rhythm and deliver electrical impulses when needed, ensuring that the heart beats at the appropriate rate for the individual's activity level.
Why Might Someone Need a Permanent Pacemaker?
Exploring Cardiac Conditions Necessitating Pacemaker Insertion
Various cardiac conditions may necessitate pacemaker insertion, such as bradycardia, heart block, and certain types of heart failure. These conditions can lead to dizziness, fainting, and fatigue due to an abnormal heart rhythm.
Assessment Before the Procedure
Before the pacemaker implantation, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including medical tests and discussions with the healthcare team to assess the need for the procedure and identify any potential risks or contraindications.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits of Permanent Pacemakers
The decision to undergo permanent pacemaker insertion involves understanding the potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes. This information is discussed with the patient to ensure informed consent.
Potential Complications Following Pacemaker Implantation
While pacemaker insertion is generally safe, potential complications such as infection, bleeding, and lead displacement may occur. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential complications and to follow post-procedure care instructions diligently.
Precautions Needed With a Permanent Pacemaker
After pacemaker insertion, patients are advised to take certain precautions, such as avoiding certain electronic devices and informing healthcare professionals about their pacemaker when undergoing medical procedures.
What to Expect During a Permanent Pacemaker Insertion Procedure?
The Pacemaker Insertion Process Step-by-Step
During the pacemaker insertion procedure, the patient is typically placed under local anaesthesia, and the device is implanted under the skin near the collarbone. The leads are carefully guided into the heart chambers using fluoroscopy, a type of X-ray imaging.
Anaesthesia and Sedation During the Pacemaker Implantation
Anaesthesia and sedation ensure patient comfort during the pacemaker insertion procedure. The type of anaesthesia used will be determined based on the patient's medical history and individual needs.
Recovery and Hospital Stay Following the Procedure
After the procedure, patients are monitored in the hospital for a short time to ensure that the pacemaker is functioning properly and that there are no immediate complications. Most patients can return home the same day or the day after the procedure.
Pacemaker Leads and Their Placement in the Heart
The precise placement of the pacemaker leads in the heart chambers is crucial for the device to monitor and regulate the heart's rhythm effectively. This placement is confirmed using imaging techniques during the procedure.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring After Permanent Pacemaker Insertion
Patients will require regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare team to monitor the pacemaker's function and ensure that it continues to meet their specific cardiac needs.
How to Prepare for Permanent Pacemaker Insertion?
Medical Tests and Evaluations Before Pacemaker Implantation
Before the pacemaker insertion, patients undergo various medical tests and evaluations to assess their overall health, check for any contraindications, and ensure that they are prepared for the procedure.
Pre-procedure Instructions and Lifestyle Modifications
Prior to the procedure, patients may receive specific instructions regarding medications, fasting, and other lifestyle modifications to ensure a smooth and successful pacemaker insertion.
Anaesthesia Considerations and Potential Medication Adjustments
The medical team will consider the patient's medical history, allergies, and current medications to determine the most suitable anaesthesia and any necessary adjustments to the patient's medication regimen before the procedure.
Discussion With the Healthcare Team Regarding the Procedure
Patients can discuss the pacemaker insertion procedure with their healthcare team, ask questions, and address any concerns regarding the implantation process and post-procedure care.
What Are the Risks and Potential Complications of Permanent Pacemaker Insertion?
Common Risks Associated With the Pacemaker Implantation Procedure
Common risks associated with pacemaker insertion include infection at the incision site, bleeding, and bruising. Proper surgical techniques and post-procedure care can minimise most of these risks.
Potential Complications During and After Permanent Pacemaker Insertion
While relatively rare, potential complications following pacemaker insertion may include lead dislodgment, infection, fever, and allergic reactions to the device materials. Some may develop flu-like symptoms. It is important for patients to be aware of these potential complications and to seek medical attention if they experience any concerning symptoms.
Emergency Situations Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
In rare cases, emergencies such as a malfunctioning pacemaker or lead displacement may occur, requiring immediate medical attention. Patients are educated on recognising signs of potential issues and seeking prompt medical care if needed.
Long-Term Concerns and Monitoring for Complications
Following pacemaker insertion, patients will require regular monitoring to ensure the continued function of the device and to address any potential long-term concerns or complications that may arise.
Interactions and Precautions With Electronic Devices and Medical Procedures
Patients with a pacemaker need to be cautious around electronic devices and other medical procedures that may interfere with the device's functioning. Individuals with a pacemaker need to inform healthcare professionals of their devices to ensure safety during medical procedures.
Conclusion
At The Harley Street Heart and Vascular Centre, our cardiologists and nurses are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for patients undergoing permanent pacemaker insertion. Our experienced team strives to ensure that each patient receives personalised attention, thorough pre-procedure evaluations, and ongoing support throughout the pacemaker implantation process. Suppose you or a loved one may require a permanent pacemaker. In that case, we are here to guide you through every step, from preparation to long-term care and monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions About PPM Insertion
Below are some of the frequently asked questions about PPM insertion.
What Is a Permanent Pacemaker Insertion?
Permanent pacemaker insertion is a procedure to implant a small electronic device in the chest to help control abnormal heart rhythms.
When Is a Permanent Pacemaker Insertion Recommended?
Permanent pacemaker insertion may be recommended for people with irregular heart rhythms or heart rate abnormalities that cannot be effectively managed with medication.
What Is Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy?
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy is a treatment for heart failure that uses a special type of pacemaker to coordinate the contractions of the heart's lower chambers (ventricles).
Who May Need Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities?
People with conditions such as heart muscle damage, heart valve problems, or certain genetic heart conditions may need device-based therapy for cardiac rhythm abnormalities.
What Are the Considerations After Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers?
After the implantation of cardiac pacemakers, precautions should be taken in activities such as cardiac catheterisation and staying inches away from certain electronic devices and magnets that can interfere with the pacemaker's function.
What Is the Relationship Between Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy?
Pacing and cardiac resynchronisation therapy are related to using implantable devices to improve the coordination and efficiency of heart contractions in people with heart failure.
What Is the Role of a Permanent Pacemaker Lead in Functioning as a Pacemaker?
The permanent pacemaker lead is a wire that connects the pacemaker to the heart and is essential for delivering electrical impulses to regulate the heart's rhythm.
When Might a Pacemaker Be Needed for a Cardiac Condition?
A pacemaker may be needed when the heart's natural electrical system is not functioning properly, leading to a slow heart rate or other rhythm abnormalities that affect the heart's ability to pump blood effectively.


