Carditis: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment

Introduction
Carditis is a term that encompasses inflammation of the heart, which can affect any of its layers: the endocardium (inner layer), myocardium (middle muscular layer), or pericardium (outer layer). This inflammation can lead to a range of serious health issues if not diagnosed and treated promptly. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of carditis, including its types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is Carditis?
Carditis refers to the inflammation of the heart and can be classified into three main types based on the specific layer affected:
- Endocarditis: Inflammation of the endocardium, the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves.
- Myocarditis: Inflammation of the myocardium, the heart muscle responsible for pumping blood.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, the protective sac surrounding the heart.
Although each type of carditis has distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches, all can seriously affect heart health.
Types of Carditis
Endocarditis

Endocarditis involves inflammation of the heart's inner lining, primarily affecting the heart valves. Bacterial infections typically cause it, though fungi and other microorganisms can also be responsible.
Causes
- Bacterial Infections: Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria are common culprits.
- Fungal Infections: Less common but can occur, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
- Intravenous Drug Use: Increases the risk of introducing bacteria directly into the bloodstream.
- Dental Procedures: Can introduce bacteria into the bloodstream, leading to endocarditis in susceptible individuals.
- Prosthetic Heart Valves: Artificial valves can be prone to infection.
Symptoms
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue and weakness
- Night sweats
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling in the feet, legs, or abdomen
- Persistent cough
- Unexplained weight loss
- New or changing heart murmurs
Diagnosis
- Blood Tests: To identify the presence of infectious organisms.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart to detect vegetation (clumps of bacteria and cells) on the heart valves.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To assess the heart's electrical activity.
- Chest X-ray: To check for heart enlargement or fluid buildup in the lungs.
- CT Scan or MRI: Advanced imaging to detect complications.
Treatment
- Antibiotics: Intravenous antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial endocarditis.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair or replace damaged heart valves.
Myocarditis
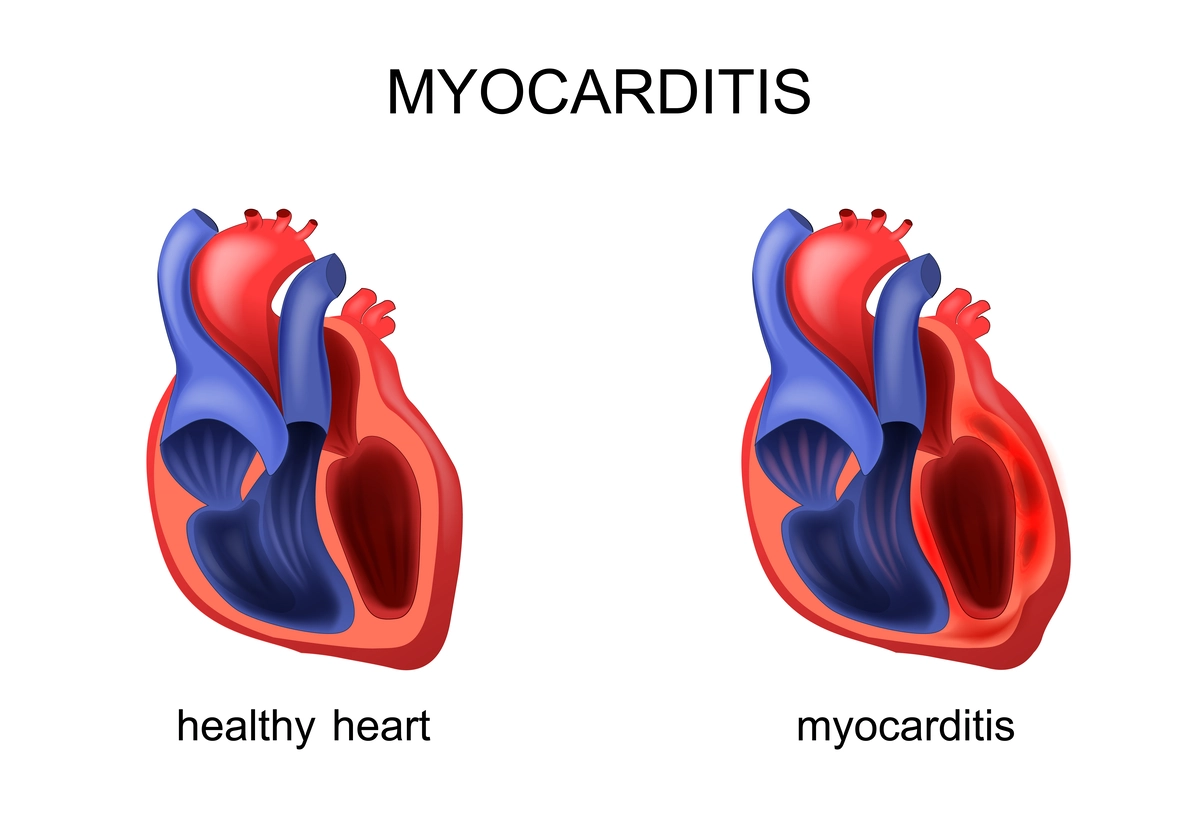
Myocarditis involves inflammation of the heart muscle, which can impair the heart's ability to pump blood and lead to arrhythmias.
Causes
- Viral Infections: Commonly caused by viruses such as Coxsackievirus, adenovirus, and influenza.
- Bacterial Infections: Less common, but can include bacteria like Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease).
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause myocarditis.
- Medications: Certain drugs can trigger an inflammatory response in the heart muscle.
- Toxins: Exposure to toxic substances like alcohol and cocaine can lead to myocarditis.
Symptoms
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Fainting or dizziness
Diagnosis
- Blood Tests: To identify markers of inflammation and infection.
- Echocardiogram: To assess heart function and detect structural abnormalities.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To detect abnormal heart rhythms.
- Cardiac MRI: Detailed imaging to visualise inflammation in the heart muscle.
- Endomyocardial Biopsy: A tissue sample from the heart muscle to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressive agents, and heart medications to manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Rest and reduce physical activity to lessen the strain on the heart.
- Surgery: In severe cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.
Pericarditis
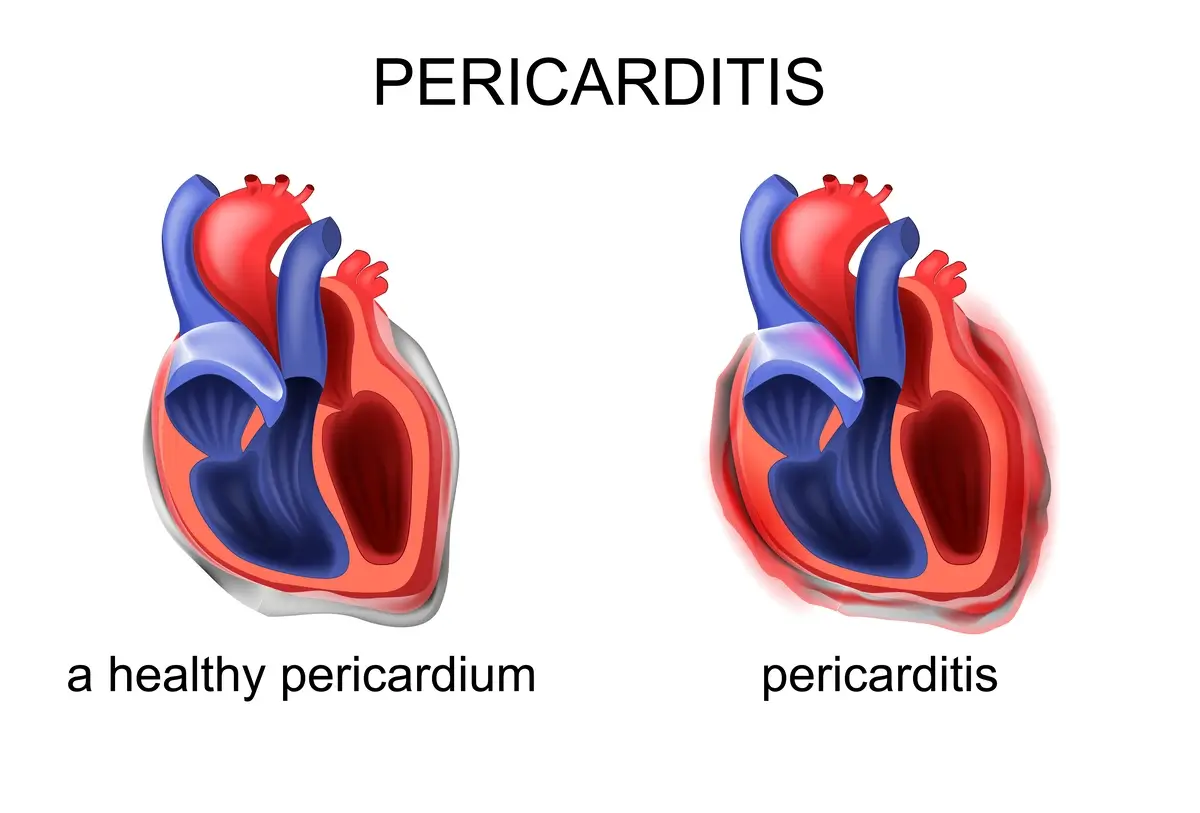
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium, the sac-like covering of the heart. It can lead to fluid buildup around the heart (pericardial effusion) and potentially cause cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening condition.
Causes
- Viral Infections: Commonly caused by viruses like Coxsackievirus and echovirus.
- Bacterial Infections: Tuberculosis and bacterial infections can cause pericarditis.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Heart Attack: Inflammation can occur after a heart attack.
- Trauma: Injury to the chest can cause pericarditis.
- Cancer: Spread of cancer to the pericardium.
Symptoms
- Sharp, stabbing chest pain that may radiate to the neck, shoulders, or back
- Pain that worsens with deep breathing or lying down
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath when reclining
- Heart palpitations
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs
Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To detect characteristic changes in heart rhythm.
- Echocardiogram: To assess fluid buildup around the heart.
- Chest X-ray: To check for heart enlargement or pericardial effusion.
- Cardiac MRI: Detailed imaging to visualise the pericardium.
- Blood Tests: To identify markers of inflammation and infection.
Treatment
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Pericardiocentesis: A procedure to remove excess fluid from the pericardial sac.
- Surgery: In severe cases, a pericardiectomy (removal of the pericardium) may be necessary.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors for carditis is crucial for prevention and management.
Infectious Causes
- Bacteria: Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Borrelia burgdorferi are common bacterial culprits.
- Viruses: Coxsackievirus, adenovirus, echovirus, and influenza virus are frequent viral causes.
- Fungi: Less common, but can include Candida and Aspergillus species.
Non-Infectious Causes
- Autoimmune Disorders: Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune conditions.
- Medications: Certain drugs can trigger inflammatory responses.
- Toxins: Alcohol, cocaine, and other toxic substances.
- Trauma: Physical injury to the chest.
- Cancer: Metastatic spread of cancer to the heart or pericardium.
Risk Factors
- Age: Older adults are more susceptible.
- Pre-existing Heart Conditions: Valvular heart disease, congenital heart defects, and previous heart surgeries.
- Immunosuppression: Weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, or immunosuppressive medications.
- Lifestyle Factors: Intravenous drug use, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking.
- Medical Procedures: Dental procedures, catheters, and implanted devices.
Symptoms
The symptoms of carditis can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever and chills
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats
- Persistent cough
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fainting or dizziness
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of carditis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications.
Blood Tests
- To identify markers of inflammation and infection.
- To detect specific infectious organisms.
Imaging Tests
- Echocardiogram: Ultrasound of the heart to assess structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To detect abnormal heart rhythms and characteristic changes.
- Chest X-ray: To check for heart enlargement or fluid buildup.
- Cardiac MRI: Detailed imaging to visualise inflammation and structural abnormalities.
- CT Scan: Advanced imaging for detailed assessment.
Specialised Tests
- Endomyocardial Biopsy: Tissue sample from the heart muscle to confirm myocarditis.
- Pericardiocentesis: Fluid sample from the pericardium to identify the cause of pericarditis.
Treatment
Carditis treatment aims to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and address the underlying cause. Options include medications, procedures, and lifestyle changes.
Medications
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
- Antiviral Drugs: For viral infections.
- Antifungal Drugs: For fungal infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids.
- Immunosuppressive Agents: For autoimmune-related carditis.
- Heart Medications: To manage heart function and rhythm issues, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or anti-arrhythmic drugs.
Procedures
- Pericardiocentesis: Draining excess fluid from the pericardial sac to relieve pressure on the heart.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These include valve repair or replacement for endocarditis and pericardiectomy for pericarditis.
- Heart Transplant: For severe myocarditis leading to heart failure unresponsive to other treatments.
Lifestyle Changes
- Rest and Reduced Physical Activity: Especially important in myocarditis to reduce the strain on the heart.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet low in sodium, saturated fats, and sugars to support overall heart health.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Smoking: Reducing or eliminating alcohol and tobacco use to prevent further damage to the heart.
- Regular Follow-up Care: Continuous monitoring and regular check-ups with a cardiologist to manage symptoms and adjust treatment as necessary.
Prevention
While not all cases of carditis can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing this condition:
Infection Control
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and maintaining good personal hygiene can prevent infections that might lead to carditis.
- Dental Care: Proper dental hygiene and regular dental check-ups to prevent infections that can spread to the heart.
- Vaccinations: Staying up to date with vaccinations, including those for influenza and other common viruses that can cause myocarditis.
- Safe Practices: Avoid intravenous drug use and ensure sterile conditions during medical procedures.
Managing Underlying Conditions
- Autoimmune Disorders: Proper management of conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis to reduce the risk of carditis.
- Heart Health: Regular monitoring and management of pre-existing heart conditions to prevent complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a balanced diet and regular physical activity to support heart health.
- Avoiding Toxins: Reducing exposure to harmful substances like alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drugs.
- Stress Management: Implementing stress-reducing practices such as meditation, yoga, or counselling to maintain overall well-being.
Living with Carditis
Managing carditis involves both medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments to support heart health and prevent complications. Here are some tips for living with carditis:
Regular Medical Care
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regularly consult your cardiologist to monitor your condition and adjust treatments as needed.
- Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications consistently and according to your doctor’s instructions.
Symptom Management
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keeping track of any changes in symptoms and reporting them to your healthcare provider.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate, doctor-approved physical activity to maintain cardiovascular health without overexerting the heart.
Support Systems
- Education: Learning about your condition and treatment options to make informed decisions.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups for individuals with heart conditions to share experiences and gain emotional support.
- Family and Friends: Enlisting the help of loved ones for emotional support and assistance with daily activities as needed.
Conclusion
Carditis, encompassing endocarditis, myocarditis, and pericarditis, is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing the disease effectively and preventing complications. By following preventive measures, seeking regular medical care, and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals with carditis can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. If you suspect you or a loved one may have carditis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional immediately for a thorough evaluation and appropriate care.


