Electrophysiology Studies | The Harley Street
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) is a cardiac test to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart and diagnose abnormal heart rhythms. The Harley Street Heart and Vascular Centre Singapore's state-of-the-art facility employs advanced technologies, including pacemaker adjustments, x-ray imaging, and cardioverter utilisation, to furnish comprehensive evaluations and tailor treatment plans to our patients.
Proceed to book an appointment for electrophysiology studies (EPS) with one of the best cardiologists in Singapore or contact us for further details to schedule your cardiac consultation.

What are Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)?
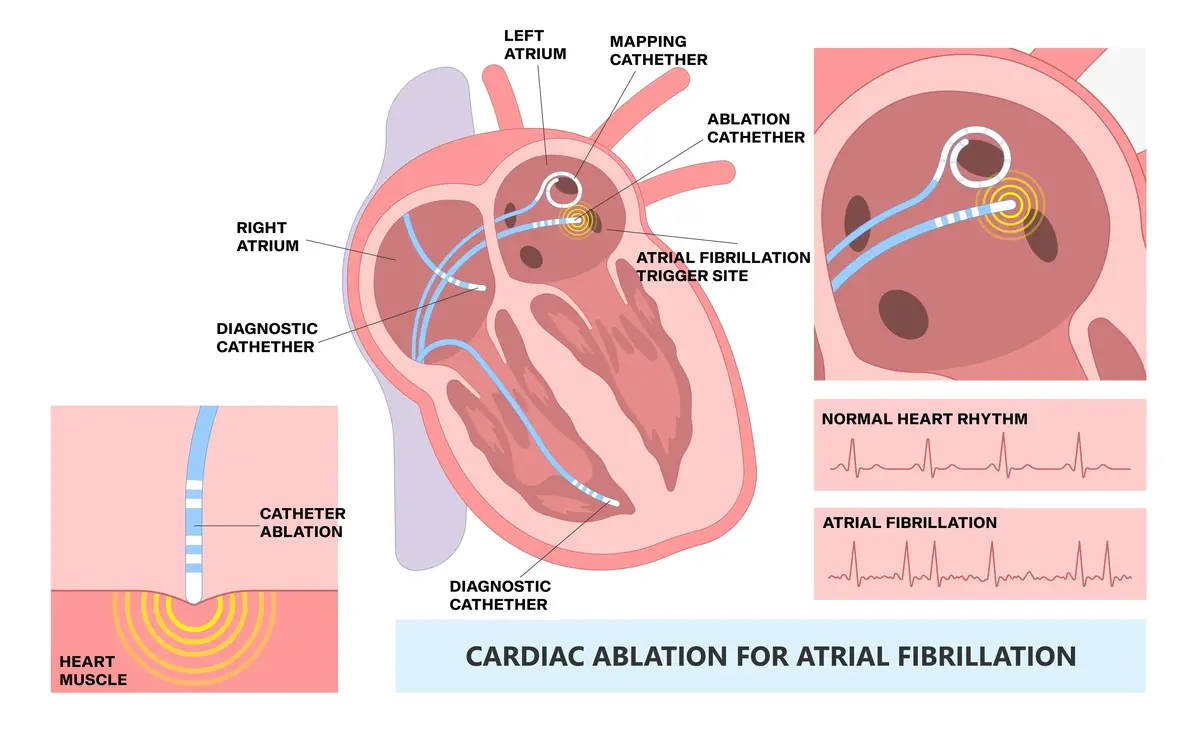
Electrophysiology studies (EPS) or electrophysiological studies (EP) are minimally invasive procedures in which thin, flexible wires (called EP catheters) are inserted from blood vessels in the leg into the heart. As with a coronary angiogram, a small part of the skin is first frozen with a local anaesthetic before the catheters are passed into the body through plastic sheaths.
Electrical stimulation of the heart through carefully placed catheters usually allows an exact diagnosis of arrhythmia. Suppose specific treatment is required to treat the arrhythmia. In that case, high-frequency electrical energy can be delivered through one of the catheters during ablation to a small area of tissue inside the heart to destroy the part that is causing the arrhythmia.
Understanding the Electrical Activity of the Heart
The heart's electrical activity plays a crucial role in regulating the rhythm of the heartbeat. Certain conditions or abnormalities in the conduction system can lead to irregular heart rhythms, affecting an individual's overall cardiac health.
How EPS Helps Diagnose Abnormal Heart Rhythms
EPS helps diagnose abnormal heart rhythms by precisely mapping and assessing the electrical activity of the heart to identify the origin and nature of arrhythmias. EPS assists in identifying the specific areas within the heart that may be causing abnormal heart rhythms, helping cardiologists devise targeted treatment plans for the patients.
Preparing for an Electrophysiology Study
Before an EPS, patients are provided with detailed instructions on the preparation process. Normally, aside from having to wear comfortable clothes, the patient needs to fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure. EPS is also often performed using light sedation. Medication adjustments are also sometimes required for a smooth and effective study. The procedure usually done by a cardiologist takes one to two hours to do. However, it can take longer, around 4 to 6 hours, if catheter ablation is required. After the study is complete, your healthcare provider will end the procedure.
Risk Factors for Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Identifying common risk factors for arrhythmias is crucial in assessing an individual's cardiac health. Factors such as family history, age, lifestyle, and underlying cardiac conditions play a significant role in predisposing individuals to abnormal heart rhythms.
Recognising Symptoms of Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Individuals need to be aware of symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath, which may indicate the presence of an abnormal heart rhythm and necessitate prompt medical attention.
Understanding the Importance of Regular Heart Rhythm Monitoring
Frequent monitoring of heart rhythm, especially for individuals with known risk factors, is essential for early detection and management of arrhythmias, reducing the risk of sudden cardiac events.
How Does Catheter Ablation Work?
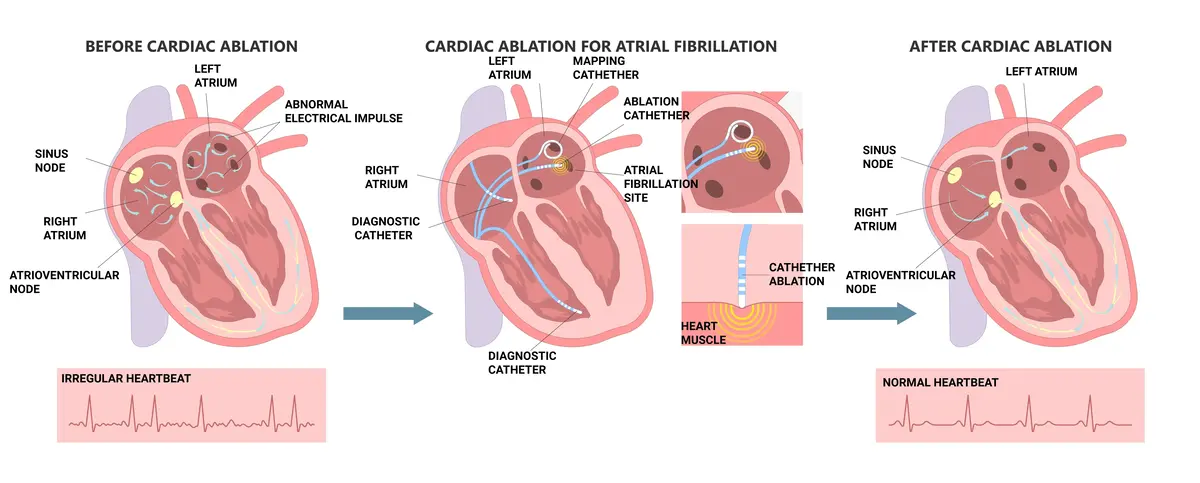
Catheter Ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the use of catheters to target and eliminate the areas in the heart responsible for abnormal heart rhythms. By delivering controlled energy, such as radiofrequency, the abnormal electrical pathways are disrupted, restoring the heart's normal rhythm. The procedure takes a short time, and after that, the doctors will remove the catheters.
Benefits and Risks of Catheter Ablation
Catheter Ablation offers a high success rate in treating certain types of arrhythmias. It can significantly improve a patient's quality of life. However, as with any medical procedure, there are associated risks that are thoroughly discussed with the patients before the intervention.
Post-Ablation Care and Recovery Process
Following Catheter Ablation, patients are provided with comprehensive post-procedural care instructions and support to promote successful recovery and long-term cardiac wellness. Post-procedural care after catheter ablation typically includes the following steps:
- Monitoring: Patients are usually monitored in a recovery room for a few hours after the procedure to ensure that there are no immediate complications or adverse reactions to the treatment. Vital signs, heart rhythm, and any potential signs of discomfort or complications are closely observed.
- Rest: Rest is important in the first 24-48 hours after the procedure. Patients are advised to take it easy and avoid strenuous activities during this time.
- Wound care: If the catheter ablation procedure requires an incision, patients will be given instructions on how to care for the wound to prevent infection and aid in healing.
- Medications: Patients may be prescribed medications to manage any discomfort or prevent complications. They must follow the prescribed medication regimen and consult their doctor if they have any concerns or experience side effects.
- Follow-up appointments: Patients will need to follow up with their healthcare provider for post-procedural appointments to monitor their progress and ensure that the procedure was successful.
In addition to these steps, patients will also receive guidance on activities to avoid, signs of potential complications, and any lifestyle changes that may be necessary to support their recovery and long-term heart health. This comprehensive post-procedural care is essential for promoting successful recovery and preventing complications after catheter ablation. Patients are encouraged to follow their care instructions closely.
Understanding the Role of Catheters in EP Studies
Catheters play a pivotal role in EP studies, enabling precise navigation and mapping of the electrical signals within the heart. As technology continues to advance, catheter-based techniques have become increasingly sophisticated in identifying and treating a spectrum of cardiac abnormalities.
Recovery After Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
The recovery after EPS is an integral part of the patient's journey, focusing on monitoring and rest to ensure a smooth transition back to daily activities. After the procedure, patients are observed for a few hours to monitor for any immediate complications. Instructions on rest, wound care, medication, and follow-up visits are provided to support the patient's recovery and long-term cardiac health. This comprehensive approach to post-procedural care is pivotal in achieving successful outcomes and maintaining heart wellness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrophysiology studies have significantly advanced our understanding of the electrical activity in the heart. They also allow us to treat many types of arrhythmia with ablation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electrophysiology Studies
Below are some of the frequently asked questions about Electrophysiology Studies.
What Is an Electrophysiology Study?
An electrophysiology study (EPS) is a test performed in the electrophysiology laboratory to assess the electrical activity in your heart. It helps in diagnosing and treating abnormal heartbeats.
Why Would I Need an Electrophysiology Study?
Your cardiologist may recommend an EPS if you have symptoms of abnormal heart rhythms, such as palpitations, dizziness, and fainting, or if you are at risk of sudden cardiac death.
How Is an Electrophysiology Study Performed?
The study is performed in a room called the cardiac EP laboratory. Thin, flexible wires called electrodes are inserted through a vein in your groin or vein in your arm and threaded into your heart to record its electrical activity.
What Is the Difference Between an Electrophysiology Study and a Cardiac Ablation?
An electrophysiology study is a test to diagnose abnormal heart rhythms, while a cardiac ablation, or catheter ablation, is a procedure done to treat these abnormal heart rhythms through radiofrequency or freezing energy. It is also known as cardiac ablation or radiofrequency ablation.
Will I Feel Any Discomfort During the Electrophysiology Study?
You may feel your heart beating or experience some discomfort when the catheters are inserted. Still, the area will be numbed, and you will be given intravenous medication to help you relax during the procedure.
What Is the Purpose of an Electrophysiology Study and Catheter Ablation?
The study and catheter ablation are performed to identify the cause of abnormal heart rhythms and, if necessary, perform the procedure to treat them.
How Long Does an Electrophysiology Study Take?
The study may take one to two hours to complete. However, the duration can vary based on the complexity of your condition and whether a catheter ablation is performed during the same session.
Is an Electrophysiology Study a Safe Procedure?
The study is an invasive test and carries some risks. Still, it is generally safe when performed by experienced professionals with the right monitoring equipment in a specialised electrophysiology laboratory.
What Should I Tell My Doctor Before an Electrophysiology Study?
You should inform your doctor about any medications you are taking, any cardiac arrhythmias, heart rhythm problems, allergies or medical conditions you have, and whether you are pregnant. It's also important to discuss any concerns or questions you may have about the procedure. You may be asked about your medical history before the procedure starts.
Where Can I Undergo an Electrophysiology Study and Catheter Ablation?
You can undergo the study and catheter ablation procedures at specialised medical centres or hospitals with cardiac electrophysiology labs, including centres like The Harley Street Heart and Vascular Centre Singapore or other reputable medical facilities.